Cannabis cultivation demands meticulous attention to detail, and one of the challenges growers may face is nutrient deficiencies in their plants. A zinc deficiency, though relatively uncommon, can have detrimental effects on your cannabis crop. In this easy-to-follow guide, Seedsman looks into the intricacies of identifying and treating a zinc deficiency in cannabis plants, covering the causes, symptoms, and effective solutions in one fell swoop. Beginner cultivators might want to bookmark this page for easy reference.
How a Zinc Deficiency Occurs:
In the human body, zinc is essential for helping fight off invading bacteria and viruses, as well as making DNA and proteins. During pregnancy and childhood, zinc helps with growth and development. In cannabis, zinc is equally important and serves as an essential micronutrient for cannabis plants, playing a crucial role in various physiological processes such as enzyme activation, DNA synthesis, and overall plant growth. In addition, zinc serves as a key driver of carbohydrate, protein and chlorophyll production. Without zinc, a plant’s growth will show as stunted, then will most likely cease entirely. Cannabis plants need a good balance of key macronutrients Nitrogen, Potasssium, and Phosphorus, known as NPK. But there are a series of helpful micronutrients including zinc, managanese, calcium and more, that help your cannabis grow and devlop healthily. Without these key ingredients, your cannabis plant may suffer from a series of symptoms that lead to damage - and nobody wants damaged plants.
A zinc deficiency occurs when the plant is unable to access an adequate amount of zinc from the growing medium. Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of a zinc deficiency:
pH Levels and Zinc Uptake:
The pH level of the growing medium plays a pivotal role in nutrient absorption, including zinc. Cannabis plants thrive in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. Deviations from this range can impede the plant's ability to take up zinc effectively. Therefore, regular monitoring and adjustment of pH levels are fundamental in preventing a zinc deficiency.


Phosphorus Antagonism:
Excessive phosphorus in the growing medium can create a competitive relationship with zinc, hindering its uptake by cannabis plants. This scenario is often encountered when growers use fertilizers with imbalanced nutrient ratios. Selecting a fertilizer specifically designed for cannabis cultivation, with careful consideration of phosphorus levels, can mitigate this issue.
Soil Quality And Microbial Activity:
The quality of the soil also influences zinc availability. Soils deficient in organic matter may lack the microbial activity necessary to convert zinc into a plant-accessible form. Introducing organic amendments such as compost and well-rotted manure enhances microbial diversity, promoting optimal zinc uptake by cannabis roots.
What A Zinc Deficiency Looks Like
Intraveinal Chlorosis
The hallmark symptom of a zinc deficiency is interveinal chlorosis, characterized by yellowing between the veins of young leaves. This indicates a disruption in chlorophyll production, leading to diminished photosynthetic capacity and overall stunted growth.
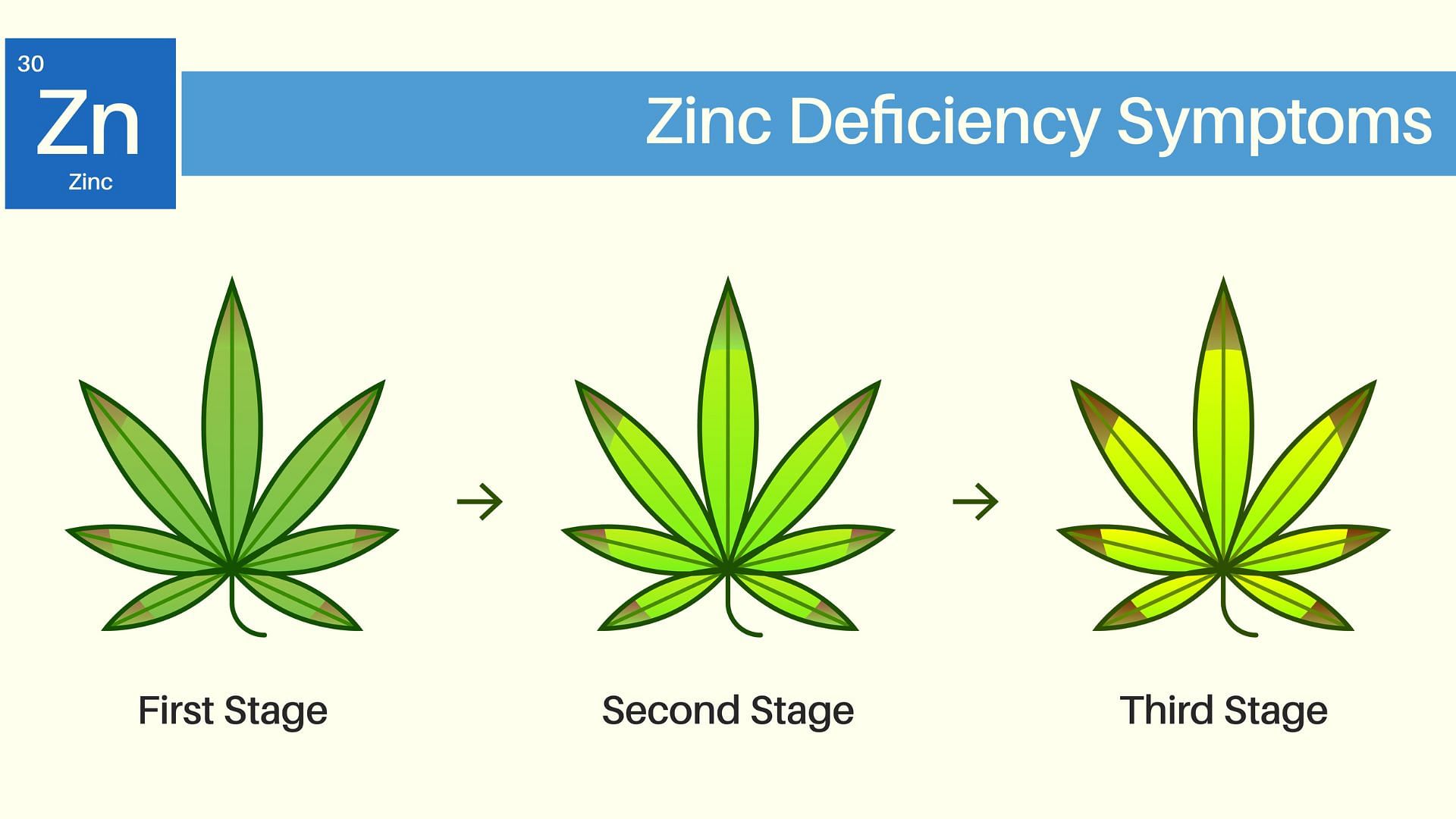

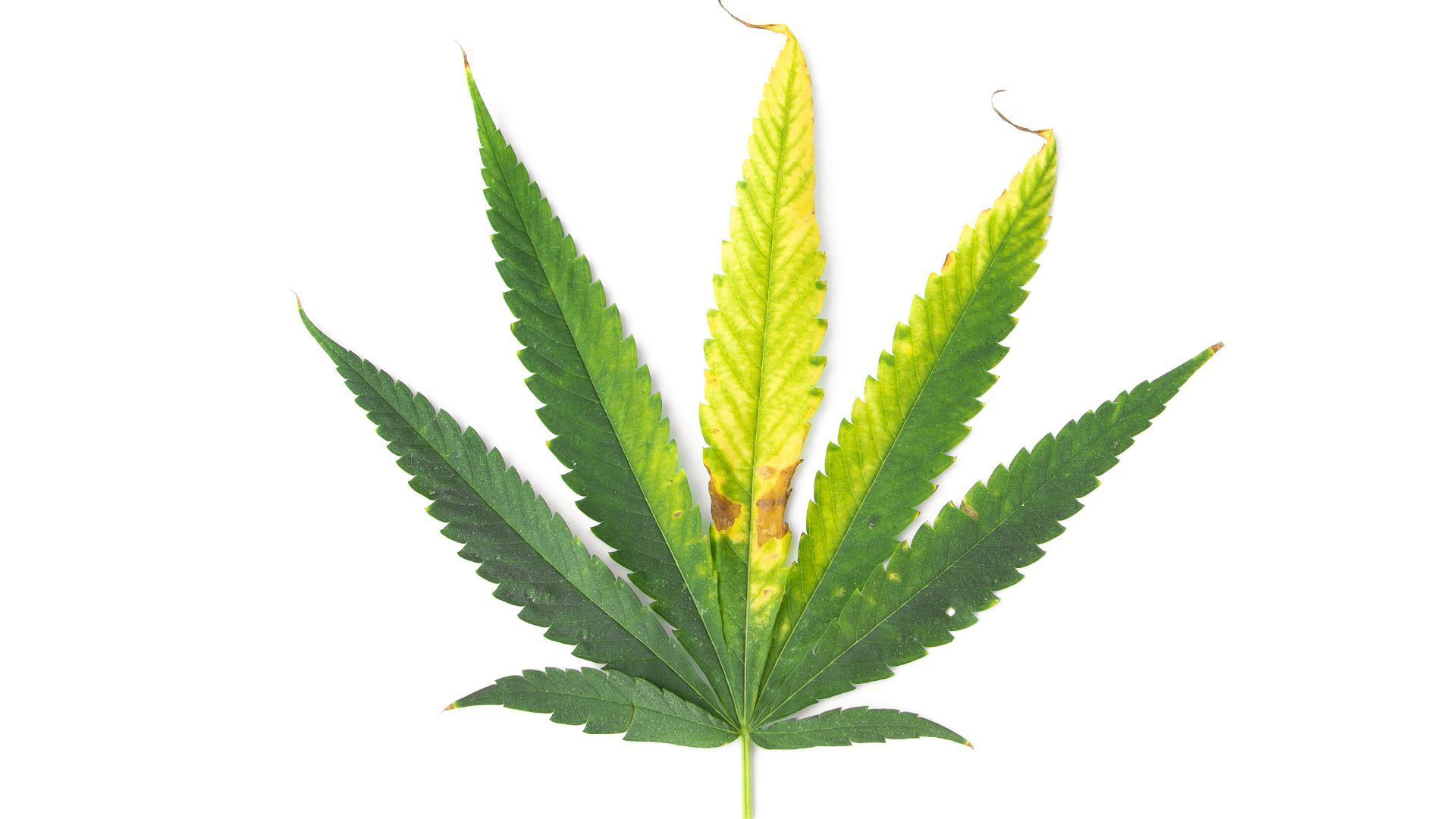
Leaf Deformation And Abnormal Growth
Cannabis plants affected by zinc deficiency often display leaves with irregular shapes and distorted growth. This deformation occurs due to the crucial role zinc plays in the regulation of plant hormones, impacting overall leaf development.


Leaf Necrosis And Tissue Death
In advanced stages of deficiency, necrotic spots may appear on the leaves, signaling tissue death. This severe manifestation can significantly compromise the plant's health, reducing both yield and potency.
When Does A Zinc Deficiency Occur?
A zinc deficiency typically becomes apparent during the early stages of the vegetative phase or as the flowering phase commences. The timing may vary based on the cannabis strain and the severity of the deficiency. Vigilant observation and early detection are paramount to implementing effective corrective measures.
How To Treat A Zinc Deficiency In Cannabis Plants
pH Management:
One of the most important steps in combatting a zinc deficiency is guarding against it. Your first step should be to regularly monitor and adjust the pH of the growing medium to maintain an optimal range of 6.0 to 7.0. This ensures the availability of zinc and other essential nutrients for absorption by the plant roots.
Balanced Nutrient Feeding:
Choose a well-balanced fertilizer formulated for cannabis cultivation. Ensure the nutrient ratios, particularly phosphorus and zinc, align with the specific needs of your plants. It’s important to follow the instructions and adjust feeding schedules based on the developmental stages of the cannabis crop.
Foliar Sprays with Zinc:
Implementing foliar sprays containing zinc is an effective method to provide a direct source of nutrients to the leaves. You want to make sure to get thorough coverage, especially on the underside of the leaves, and repeat applications as necessary until symptoms abate.
Organic Amendments for Soil Improvement:
Enhance your soil’s quality by incorporating organic amendments such as compost, well-rotted manure, or other organic matter. This fosters a healthy microbial environment, promoting the conversion of zinc into a plant-available form. If you’re using a good quality soil from the outset, this won’t be as much of an issue.


Chelated Zinc Supplements:
Opt for chelated zinc supplements, which are more readily absorbed by plants. These supplements can be added to the nutrient solution or directly applied to the soil, providing a quick and efficient means of addressing the deficiency.
Advanced Techniques for Treating Zinc Deficiency
Hydroponic Systems:
In hydroponic setups, maintaining precise nutrient concentrations is crucial. Use high-quality hydroponic nutrient solutions with well-defined zinc content to prevent deficiencies in cannabis plants.
Precision Agriculture Technology:
Utilize precision agriculture tools such as nutrient sensors and monitoring systems to track zinc levels in real-time. This data-driven approach is decidedly more high-tech and involves a good degree of monitoring, but it allows growers to make timely adjustments to nutrient solutions, ensuring optimal plant nutrition.
Conclusion
As it’s a micronutrient, zinc deficiencies are relatively uncommon in cannabis plants. Nonetheless, cultivating robust and high-yielding cannabis plants demands a comprehensive understanding of nutrient management, and zinc plays a pivotal role in this intricate process. By recognizing the causes and symptoms of a zinc deficiency, growers empower themselves to take proactive measures to address the issue. Whether through pH management, balanced nutrient feeding, foliar sprays, organic amendments, or advanced techniques, the key is to tailor solutions to the specific needs of the cannabis crop. As cultivators continue to refine their skills, the journey towards cultivating healthy and thriving cannabis plants becomes a rewarding pursuit, with each harvest a testament to their dedication and expertise.


