For cannabis growers looking to achieve healthy plants with high yields, understanding plant nutrition is non-negotiable. Equally important is the ability to understand when your plants are trying to communicate a problem to you – failure to recognize the signs and symptoms of common cannabis leaf problems and act accordingly can spell disaster for your crop.
One of the more misunderstood yet crucial cannabis nutrients is phosphorus – a vital macronutrient that, when deficient, can dramatically impact a cannabis plant’s health, development, and final harvest quality.
Cannabis phosphorus deficiency is a relatively common issue, particularly among indoor growers and those using organic or soilless mediums, where nutrient levels can fluctuate quickly. If left unchecked, phosphorus deficiency can stunt growth, reduce bud production and result in poor resin development. This guide explores the importance of phosphorus, how to identify a cannabis phosphorus deficiency, when plants need it most, and most importantly, how to fix it effectively.
Why Phosphorus is Important for Cannabis Plants

Phosphorus (P) is one of the three primary macronutrients essential for plant growth, alongside nitrogen (N) and potassium (K). In the context of cannabis cultivation, phosphorus plays several critical roles:
Energy Transfer: Phosphorus is a key component of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy molecule that fuels every major function of the plant. Every biological process that requires energy – such as photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and cell division – relies on ATP.
Root Development: Cannabis root health depend on phosphorus. During early vegetative stages, phosphorus drives root expansion and helps cannabis seedlings establish a stable foundation.
Flower Formation: As cannabis transitions into its flowering stage, phosphorus becomes even more crucial. It fuels the development of buds, enhances terpene and cannabinoid production, and promotes overall bloom density.
Genetic and Enzymatic Function: Phosphorus is a structural element of DNA and RNA, making it essential for cell division and plant reproduction.
Put simply – if your cannabis plants don’t have enough phosphorus, they won’t grow properly – and they definitely won’t flower to their full potential.
When Do Cannabis Plants Need Phosphorus the Most?

Cannabis plants require phosphorus throughout their lifecycle, in varying amounts, but the demand intensifies at specific phases. Identifying your plant's nutritional needs at each stage of growth is vital to ensuring they reach their potential.
Early Vegetative Stage: While nitrogen requirements dominate the early veg phase, phosphorus is critical for establishing a robust root network. This early investment in root healthy will directly affect the plant’s ability to uptake water and nutrients later.
Transition to Flowering: As your plants shift from vegetative growth into flowering, their need for phosphorus spikes. This is when plants reallocate resources toward reproductive growth, and phosphorus plays a direct role in the formation of pre-flowers and bud sites.
Peak Flowering: In mid-to-late bloom, phosphorus is needed to support the continued development of dense, resinous flowers. A lack of phosphorus here will directly impact your harvest weight and potency.
If you’re following a feed schedule, be sure to increase phosphorus content during pre-flower and continue strong phosphorus support during flowering.
What Does a Cannabis Phosphorus Deficiency Look Like?
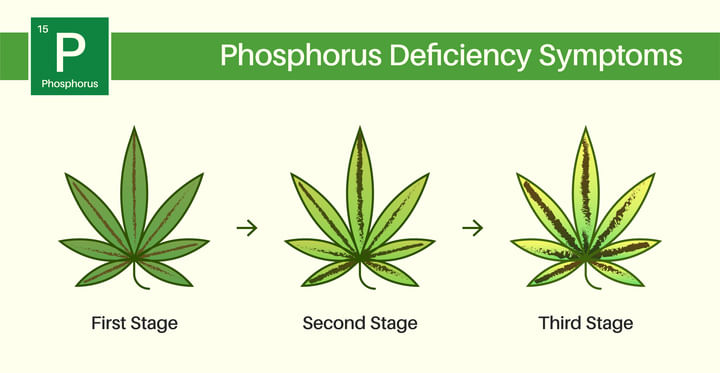
Cannabis phosphorus deficiency manifests in several visible and physiological ways. Unlike nitrogen deficiencies, which often affect the upper canopy first, phosphorus deficiencies typically show up in the older, lower leaves of the plant. It doesn’t always scream for attention right away, but over time it becomes unmistakable. Here’s what to look out for:
Darkening and Purpling: Leaves may darken to a bluish-green or take on a purple or reddish hue, especially in the stems and leaf veins. This is not to be confused with purple strains, which exhibit color changes due to genetics, not deficiency.
Slow or Stunted Growth: A phosphorus-deficient plant may grow slowly or appear to be “paused”. Bud development can also stall.
Necrotic Patches: Over time, affected leaves may develop brown, bronze, or gray necrotic spots that eventually lead to leaf death.
Weak Roots and Thin Stems: Without enough phosphorus, root systems may be underdeveloped, and stems may become thin, brittle, or discolored.
What Causes Phosphorus Deficiency in Cannabis?
A cannabis phosphorus deficiency may be the result of more than just low phosphorus in your feed. Common causes include:
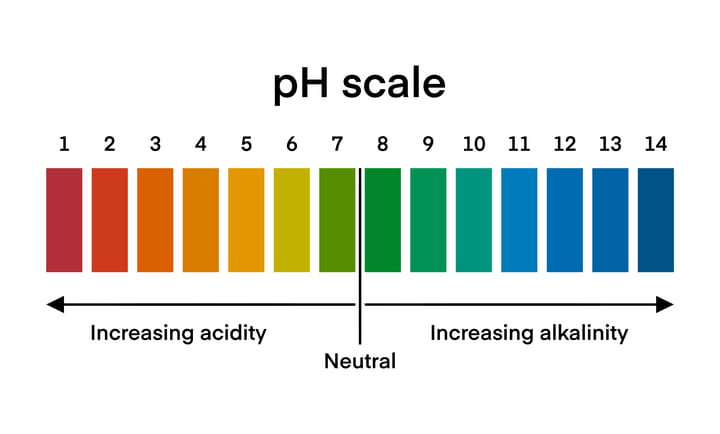
Incorrect pH Levels: Cannabis plants absorb phosphorus most efficiently within a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0 in soil and 5.5. to 6.5 in hydroponics. Outside of these ranges, phosphorus becomes chemically unavailable.
Cold Temperatures; Low root zone temperatures (below 15C or 59F) can reduce phosphorus uptake significantly, even if there’s plenty available in the soil.
Overwatering: Saturated root zones can limit oxygen availability and disrupt nutrient absorption, including phosphorus.
Poor Soil Quality: Organic soils lacking microbial life may not break down phosphorus into plant-available forms.
Nutrient Imbalance: Excess levels of iron, zinc, or calcium can lock out phosphorus through antagonistic interactions.
How To Fix Cannabis Phosphorus Deficiency
Now for the good news: While a cannabis phosphorus deficiency can cause a number of problems for your plants, it’s fairly straightforward to diagnose and correct via a targeted response. If you find your plants showing the signs of a phosphorus deficiency, here’s how to restore balance:
Check and Adjust pH
This is the first and most crucial step. If the root pH is off, phosphorus won’t be absorbed, no matter how much you feed. Use a calibrated pH meter or soil probe to measure pH levels, and depending on results, you can use pH up/down solutions to bring it back to the sweet spot.
For soil, adjust the pH to 6.2-6.8
For hydro or coco, aim for 5.8-6.2
Flush with pH-balanced water if you’re seeing nutrient lockout symptoms.
Use Organic Fertilizers

It's tempting to apply a bloom stage nutrient formula high in phosphorus, but synthetic fertilizers are generally best avoided. They can ruin the soil microbiome, and limit the efficacy of beneficial microbes. That's a problem, because it makes it harder for your plants to absorb nutrients and make it easier for them to become diseased. Instead, amend with:
- Bat Guano (especially high-phosphorus variants)
- Bone Meal
- Rock phosphate (slow release)
- Fish Bone Meal
Hydro growers can use liquid formulas like monopotassium phosphate (MKP) for fast uptake.
Warm The Root Zone
If you’re growing in cold conditions, there’s always the possibility that the root temperature is too low to allow adequate phosphorus uptake. If this is the case, you can use heating mats or insulation to keep root temps above 18C (64F). This significantly improves phosphorus uptake.
Improve Soil Microbial Health
Healthy soil biology helps break down organic phosphorus into usable forms, so consider using specific amendments to optimize your medium, such as:
- Mycorrhizal Fungi
- Compost Teas
- Worm Castings
These amendments enhance root interaction with phosphorus and other nutrients.
Avoid Overwatering
Careful watering is essential for many reasons, and correcting or avoiding a phosphorus issue is one of them. Allow the topsoil to dry between waterings to prevent root suffocation and nutrient lockout. A healthy wet-dry cycle promotes better nutrient absorption.
Cannabis Phosphorus Deficiency: Prevention beats Cure
While treatment is possible, it’s obviously far better to prevent cannabis phosphorus deficiency through proactive practices:
- Feed plants appropriately according to growth stages
- Regularly monitor and correct your pH
- Choose high-quality, well aerated grow media
- Keep environmental conditions (especially temperature) stable.
By understanding when and why cannabis plants need phosphorus, growers can ensure their crop thrives through every stage – from seedling to sticky, trichome-laden colas.
Final Thoughts
Cannabis phosphorus deficiency can be a silent yield killer if left unchecked. It often starts subtly, showing up as slow growth or minor discoloration, but its long-term impact on root health, bud development, and potency can be devastating. Fortunately with the right knowledge and proactive care, phosphorus issues can be corrected – and even prevented entirely.
As cannabis cultivation continues to evolve, so must our understanding of plant nutrition. Stay observant, act early, and give your plants the phosphorus they need when they need it most. Your yields – and your smoke – will thank you for it.


