The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a crucial role in maintaining physiological homeostasis in the body. Endocannabinoid deficiency is a relatively new concept that suggests that some people may have a deficiency in their endocannabinoid system, which could lead to various health issues. The idea of endocannabinoid deficiency was first proposed by Dr. Ethan Russo, a neurologist and cannabis researcher, in 2004. Since then, research in this area has been limited, but it has sparked interest in the medical community.
The concept of endocannabinoid deficiency is based on the idea that the endocannabinoid system may play a role in several medical conditions, including migraine headaches, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, and other chronic pain disorders. Research has shown that the endocannabinoid system is involved in pain modulation, inflammation, and stress responses, but in some individuals, the lack of a functioning ECS can trigger these conditions.
What Is The Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex biological signaling network that plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis, or internal stability, in the body. The ECS is involved in various physiological processes including:
- appetite and digestion
- metabolism
- pain recognition
- inflammation and other immune system responses
- mood
- learning and memory
- motor control
- sleep
- cardiovascular system function
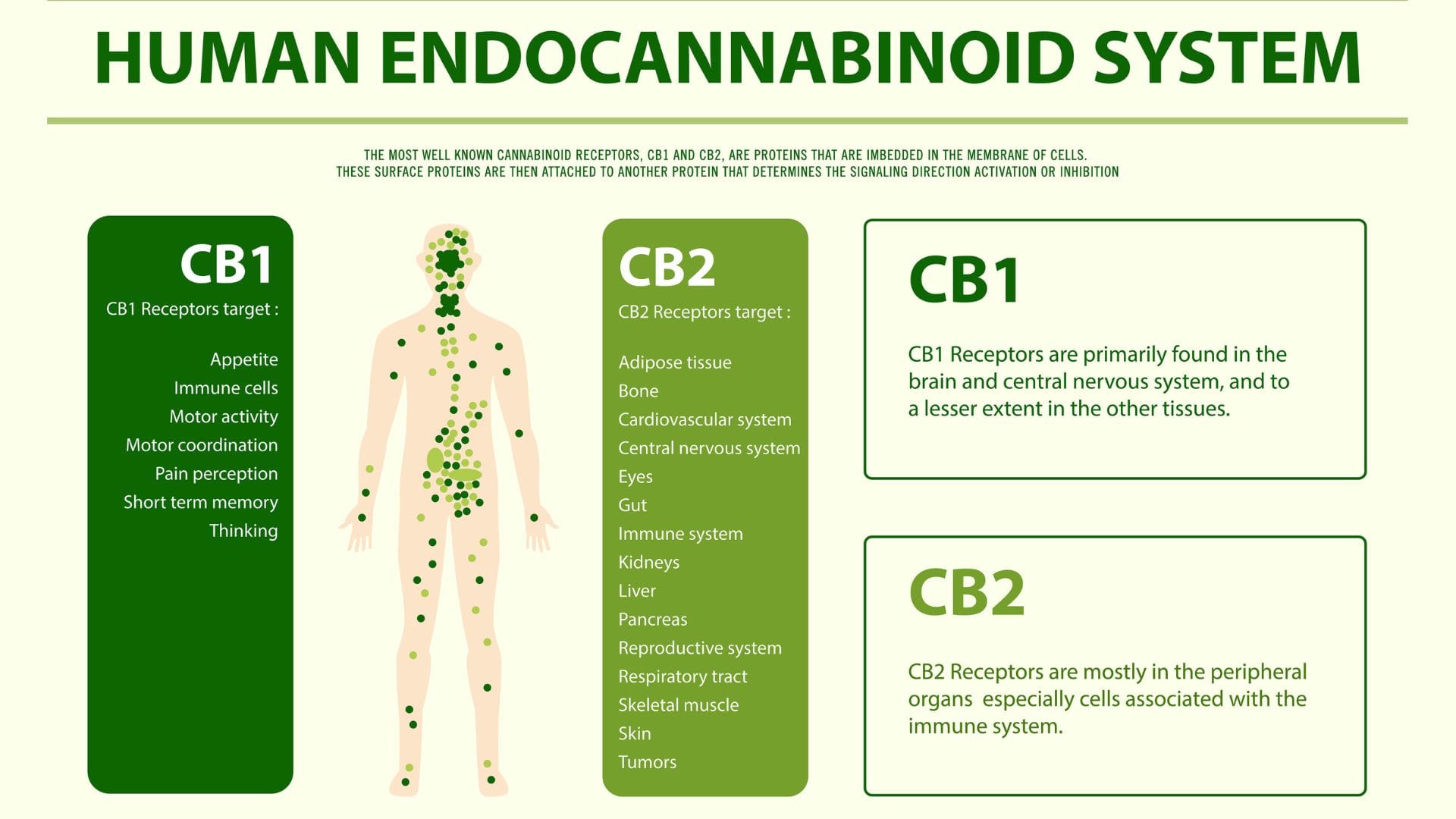

Endocannabinoids are the body's natural cannabinoids that bind to cannabinoid receptors in the ECS. Our bodies produce molecules called endocannabinoids, structurally similar to the molecules in the cannabis plant, to stimulate these receptors.
These receptors are labeled CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are found mainly in the brain and central nervous system, with CB2 receptors mostly found in the peripheral organs (especially in the immune cells). Endocannabinoids bind to these receptors, producing different results depending which endocannbinoids binds to which receptor. For example endocannabinoids may bind to a CB1 receptor to relieve pain.
The two key endocannabinoids identified to date are:
- Anandamide (AEA)
- 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG)
Anandamide is thought to regulate the brain’s reward circuitry, leading to its being dubbed “the bliss molecule”. It’s thought to play a role in how we experience the euphoric effects of certain drugs.
2-AG plays an altogether different role, and is thought to influence emotion and cognition among other things. Scientists at the University of Tokyo discovered that elevated levels of 2-AG can decrease the occurrence of seizures.
What Is Endocannabinoid Deficiency?
Endocannabinoid deficiency is a relatively new concept first proposed in 2004 by Dr. Ethan Russo, a neurologist and cannabis researcher.
The term describes a condition where the endo cannabinoid system is unable to produce enough natural endocannbinoids - and while it’s still not an officially recognised medical condition, there is significant evidence in support of its existence.
- The deficiency is said to occur when the ECS is out of homeostasis, which can happen due to several reasons:
- The body is not producing enough endocannabinoids
- There are too many enzymes in your ECS, causing a quicker breakdown of endocannabinoids
- Communication between endocannabinoids and receptors is flawed, causing the brain to struggle processing signals from neurotransmitters.
Russo hypothesized that decreased functionality of the ECS is at the root of several conditions, chiefly:
- Migraines
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
- Clinical Depression

Russo partly based this on the fact that these four conditions often appear as a cluster of symptoms in patients who display endocannabinoid deficiency. Studies following Russo’s 2004 paper seemed to support this, and would go on to link endocannabinoid deficiencies to a host of other conditions including epilepsy,autism, and PTSD.
Research in this area has been limited, but it has sparked interest in the medical community. Scientists have identified certain mutations in the amino acid sequences that encode cannabinoid receptors, as well as in the metabolic enzymes responsible for regulating cannabinoid levels. Evidence suggests that genetic variants may well predispose certain people to certain diseases.
Causes of Endocannabinoid Deficiency
Endocannabinoid deficiency can be caused by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and diet. Habits such as poor diet, lack of sleep, failure to exercise and drug abuse are all identifiable markers in causing chronic stress, which can, in turn, deplete endocannabinoid tone. The result is an increased susceptibility to certain ailments. On the genetic front, studies have shown that mutations in genes responsible for the production, degradation, and transportation of endocannabinoids can lead to lower levels of endocannabinoids in the body.
Diet is another important factor in maintaining a healthy ECS. Studies have shown that a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids can help to stimulate the production of endocannabinoids. On the other hand, a diet high in saturated fats and sugar can lead to a decrease in endocannabinoid production.
Symptoms of Endocannabinoid Deficiency
The symptoms of endocannabinoid deficiency can vary depending on the individual. Some of the most common symptoms of endocannabinoid deficiency include chronic pain, migraines, anxiety, and depression. Clinical Endocannabinoid Defiency is difficult to diagnose, as, while there are tests to measure encodannabinoid levels in the body, none of these are subject to official medical procedures. For that reason, CECD remains a theory, albeit one with some testing behind it.
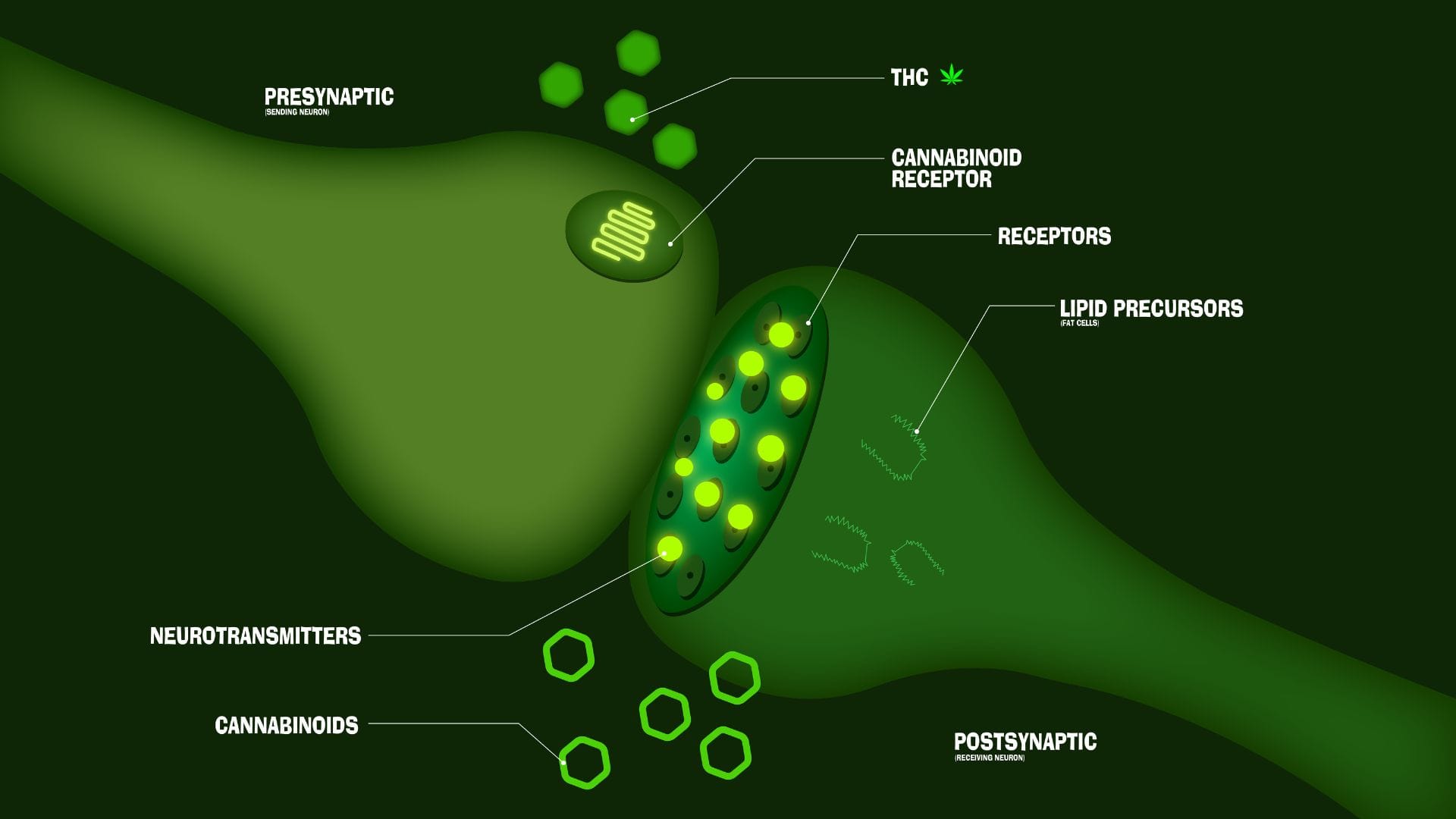

Chronic pain is among the most common symptoms of endocannabinoid deficiency. Endocannabinoids are involved in the regulation of pain perception, and low levels of endocannabinoids can lead to chronic pain conditions. Migraines are another common symptom of endocannabinoid deficiency, as endocannabinoids are involved in the regulation of blood flow, and low levels of endocannabinoids can lead to migraine headaches.
Anxiety and depression are also common symptoms of endocannabinoid deficiency. Endocannabinoids are involved in the regulation of mood, and low levels of endocannabinoids can lead to anxiety and depression.
Common Misconceptions about Endocannabinoid Deficiency
There are several common misconceptions about endocannabinoid deficiency that need to be addressed. One of the most common misconceptions is that endocannabinoid deficiency is a condition that affects only cannabis users. While cannabis use can lead to a temporary decrease in endocannabinoid production, endocannabinoid deficiency is not exclusive to cannabis users.
Another common misconception about endocannabinoid deficiency is that it is a rare condition. While there is still much to learn about endocannabinoid deficiency, studies have shown that it may be more common than previously thought.


It’s also not true that if someone has an endocannabinoid deficiency, it cannot be treated. Supplementing with exogenous cannabinoids, such as CBD and THC, can help to address the problem. This works by assisting the expression of endocannabinoids in the brain, and increasing the levels of 2-AG, preventing them from breaking down.
Finally, there is a common misconception that supplementing with exogenous cannabinoids is the only way to address endocannabinoid deficiency. While supplementing with exogenous cannabinoids may be helpful for some individuals, there are other ways to support a healthy ECS, such as through exercise, diet, and stress reduction techniques. It's thought that a diet high in nutrient-dense foods can help.