For growers aspiring to achieve higher yields and healthier cannabis crops, understanding and maintaining the correct soil pH levels is paramount. The pH level - a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution - directly influences the availability of nutrients to your plants and the thriving microorganisms in your soil. With optimal pH levels, cannabis plants can uptake nutrients efficiently, resulting in healthy growth and plentiful harvests. This tutorial will take you through the process of measuring pH levels in cannabis soil, including various techniques, equipment options, and the ideal frequency for soil testing. You can ensure a successful and prosperous growing journey by equipping yourself with the right tools and knowledge to manage soil pH.
Osmosis And pH
The pH level in soil affects both the solubility of nutrients and the osmotic balance in plants. Osmosis is the movement of water across membranes, driven by concentration differences (nutrients, salts, pH etc). pH imbalances can alter nutrient availability, thereby affecting the osmotic potential within plant cells. If pH is too high or low, certain nutrients become less accessible, influencing the plant's internal osmotic pressure. This affects water and nutrient uptake and overall plant health. pH also impacts membrane proteins like aquaporins, essential for water transport, further linking pH to osmotic regulation. Therefore, pH control in growing mediums is vital for optimal plant growth.
The Role Of pH Levels In Cannabis Cultivation
The pH scale runs from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Anything below 7 is considered acidic, and anything above is alkaline (or basic). Tap water, for example, is typically fairly pH neutral and should range from 6..5 to 9.5. Soil pH is a critical element in determining the ability of your cannabis plants to access and absorb nutrients in the soil. For soil-based cannabis growth, the ideal pH falls slightly on the acidic side, ranging from 6.0 to 7.0. The best pH range for hydroponic or soilless growing mediums is between 5.5 and 6.5.
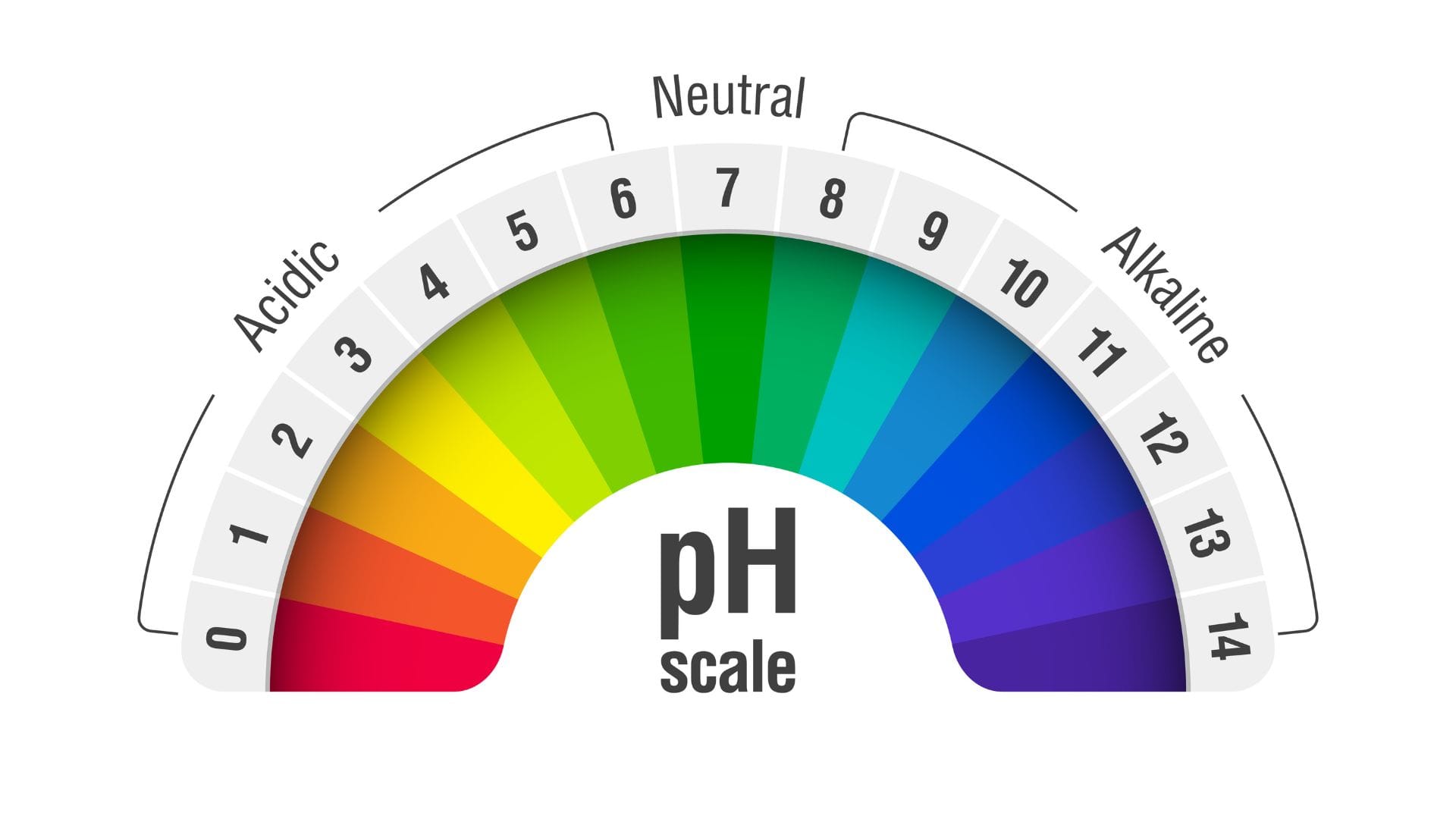

Maintaining pH within these optimal ranges allows cannabis plants to maintain water turgur pressure, which keeps plants taut and upright, allowing them to open and close stomata, and absorb the necessary macro and micronutrients effectively. Nutrient solubility can be affected if the pH deviates outside this range, making them less available to the plants. This situation can result in nutrient deficiencies, inhibiting growth, negatively impacting plant health, and ultimately reducing crop yields.
Techniques For Measuring pH Levels In Cannabis Soil
Soil can be prone to pH fluctuations, so monitoring levels is vital. Some small fluctuations are expected, and your plants will tolerate them, but if the pH strays too far from the optimal range, your plants can experience problems. Fortunately, several techniques are available to measure the pH levels in cannabis soil. Each method has its advantages, and the choice largely depends on your budget, need for accuracy, and personal preference.
1. pH Test Strips: This method, known as the litmus paper method, is a basic and cost-effective way to test soil pH. A strip of specially treated paper is inserted into a soil-water mixture. The paper changes colour according to the pH level of the solution, and the colour is then matched with a colour chart to estimate the pH value. While pH test strips are an economical option, their accuracy is inferior to that of more advanced methods.


2. pH Meters: A pH meter provides a digital and precise measurement of soil pH. The device features a probe which inserts directly into the soil or a soil-water mixture. Although pH meters are typically more expensive than pH strips, their increased accuracy and convenience make them a preferred choice among many cultivators. Some pH meters also have additional features like backlit displays and waterproofing, making them more user-friendly.


3. Soil pH Testing Kits: These kits are a more comprehensive tool for measuring pH. A soil pH testing kit typically contains a pH-reactive solution and a colour chart. When you mix the solution with a soil sample, it changes colour based on the soil's pH. Comparing this colour change with the included chart estimates the soil's pH level. Soil pH testing kits tend to be more accurate than pH strips and cheaper than pH meters.
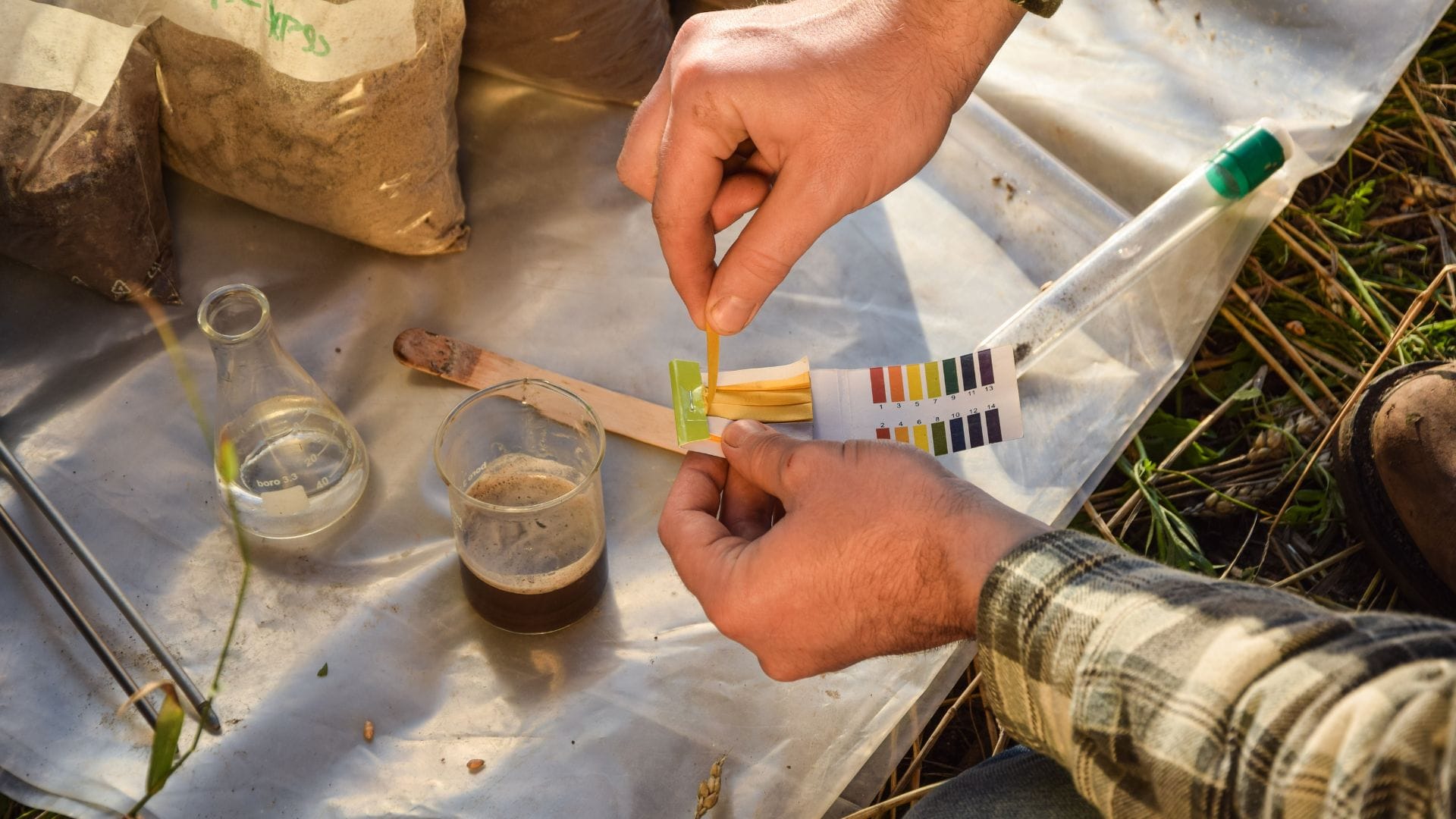


Once you’ve taken pH readings, you can then take steps to correct pH imbalances. There are a few options for pH adjusters, depending on whether the pH is too low or too high.
If pH Is Too High
1. Sulfur: Adding elemental sulfur to the soil is a common method to lower pH levels. When sulfur is mixed into the soil, it undergoes a gradual oxidation process, producing sulfuric acid, which helps acidify the soil.
2. Peat Moss and Organic Matter: Incorporating peat moss or organic matter into the soil can lower pH levels. These naturally acidic materials can help buffer the soil towards a more favourable pH range for cannabis.
3.pH-Adjusting Fertilisers: Some fertilisers are specifically designed to lower soil pH. Look for products containing ammonium-based nitrogen, which releases acidifying ammonium ions as the plant consumes the nitrogen.
If pH Is Too Low
1. Agricultural Lime: Agricultural lime, also known as garden lime, dolomite lime, or calcium carbonate, is a popular option to raise soil pH. It neutralises acidity by releasing calcium and reducing the concentration of hydrogen ions.
2. Wood Ash: Wood ash can naturally elevate pH levels, as it contains potassium and other alkaline compounds. However, it should be used cautiously, as excessive amounts can cause an imbalance of nutrients.
3. Baking Soda: Baking soda is alkaline and will reduce slightly acidic soil.
4. pH-Adjusting Fertilisers: Certain fertilisers are formulated to raise soil pH. Look for products containing nitrate-based nitrogen, which releases basic nitrate ions as the plant consumes the nitrogen.
When To Test Your Soil’s pH
Consistency in monitoring soil pH is a crucial component of successful cannabis cultivation. Generally, it is advisable to check the pH of your soil at least once a week. If your plants are displaying signs of nutrient deficiency or other related issues, it might be beneficial to increase the frequency of testing.
It is crucial to remember that activities such as watering, fertilising, and natural biological processes can alter your soil’s pH. Therefore, frequent testing will ensure you catch any deviations in pH promptly, allowing you to take corrective action before your plants suffer.
Conclusion
Understanding how to measure and manage the pH levels in your soil can significantly impact your cannabis growing success. By utilising the appropriate techniques and equipment, you can maintain an optimal pH environment for your plants, fostering healthier growth and superior yields. Regularly testing your soil’s pH will allow you to catch any imbalances early, enabling you to adjust conditions before your plants suffer adverse effects. With the right knowledge and tools, you can confidently manage your cannabis soil's pH levels, ensuring a vibrant, productive crop.


