When you look at a thriving weed plant, basking under the sun or glowing beneath full-spectrum LEDs, you’re witnessing one of nature’s most elegant power exchanges in motion. While it may seem like the plant is simply ‘growing’ - thickening stems, pushing out leaves, and stacking on buds – under the surface, an incredible biological process is unfolding. Light is being transformed into matter; into sugars, cannabinoids, terpenes, and ultimately, into the very thing we grind, roll, and light.
At the heart of it all is photosynthesis, a process as ancient as life itself, yet still brimming with scientific intrigue. And for cannabis – a plant renowned for both its agricultural complexity and psychoactive sophistication – the way it uses light is especially fascinating.
What’s happening when your weed plant stretches toward the sun? When plants convert light, the energy is stored as biochemical energy in plant cells, fueling all aspects of growth. Why does blue light produce bushier growth, while red light triggers blooms? And how can understanding these light-driven mechanics turn a good harvest into a great one?
It’s time to demystify the science of photosynthesis in cannabis. From the chloroplasts in each leaf to the intensity of photons hitting your grow tent canopy, we’ll illuminate the entire journey light takes to become the fuel of the flower.
What Is Photosynthesis?

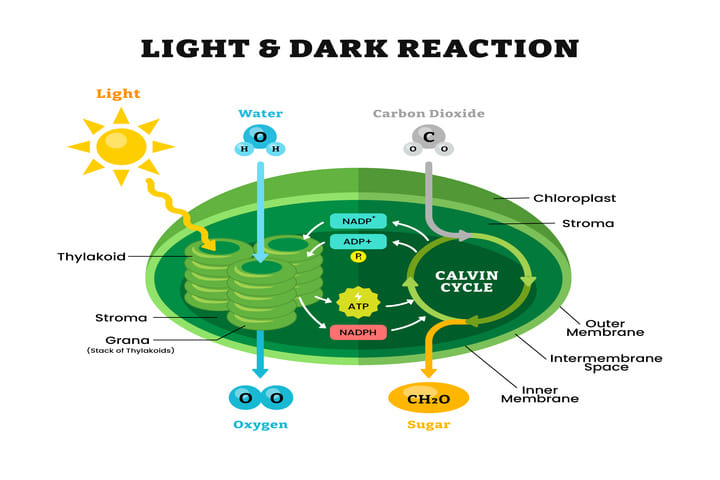
Like other plants, cannabis relies on chlorophyll molecules to absorb light and drive photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is how plants turn light, carbon dioxide, and water into sugar and oxygen. Think of it as a kind of natural cooking; light is the heat, the air and water are the ingredients, and the final dish is the energy for your plant to use. Only photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)—the specific range of light wavelengths from 400 to 700 nm—can be used by plants in this process.
In simple terms:
Light + CO2 + H20 = Sugar + 02
For the weed plant, this sugar isn’t just energy – it fuels stem growth, leaf production, root expansion, and even the formation of cannabinoids like THC and CBD. At the same time, oxygen is released as a byproduct, benefitting everything from humans to animals.
There are two key phrases in this process:
Light-dependent reaction: Light energy splits water molecules, releasing oxygen and creating ATP and NADPH, the plant’s energy molecules. The speed of photosynthesis (photosynthesis speeds) during this stage can be influenced by the amount and quality of available light.
Calvin cycle: The plant uses that stored energy to convert CO² into sugars. For optimal photosynthesis, it is important to consider how much light is provided, as only the light emitted within the PAR range is effective for this process.
As an example, if the available light in a grow room is increased within the PAR range, the rate of photosynthesis in a cannabis plant can rise, leading to faster growth and potentially higher yields.
Why Light Spectrum Matters for your Weed Plant
Not all light is created equal. The light quality is crucial in determining how effectively a weed plant can photosynthesise, as different lighting options vary in their ability to drive plant growth and cannabinoid production. Plants, including cannabis, use light in the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) range – wavelengths between 400 and 700 nanometres.

Each part of the light spectrum plays a different role in the growth of a weed plant:
Blue light (400-500nm) helps produce short, bushy plants with strong leaves and stems – perfect for weed plants in veg.
Red light (600-700nm) encourages stretching and flowering- ideal for weed plants in the bloom stage.
Far-red light (700-750nm) can help trigger flowering through the plant’s internal light-detection system (the phytochrome network).
There is a noticeable contrast between various grow lights in terms of their spectral output and effectiveness for cannabis growth, which impacts how efficiently plants photosynthesise under different lamps. That’s why many grow lights combine blue and red, creating a full-spectrum environment that mimics sunlight and supports all growth phases. Some modern LEDs also include UV and infrared light to enhance trichome production and terpene profiles.
Further Reading:Understanding Light Spectrums In Cannabis Cultivation

When measuring light for plant growth, photosynthetic photon flux densities (PPFD) are used to quantify the amount of usable light reaching the plant, helping growers optimise conditions for maximum yield.
Light Intensity and Duration: Getting it Just Right For Weed Plants
Light intensity is measured in PPFD – photosynthetic photon flux density. It refers to how many photons of light hit each square metre of your weed plant every second.
Here’s a simplified range to aim for:
Seedlings: 200-400 umol/m2/s
Vegetative growth: 400-700 umol/m2/s
Flowering: 800-1,200 umol/m2/s
Your weed plant loves strong light – up to a point. If intensity is too low, your plant stretches and under-produces. Too high, and you risk light stress or heat damage (especially without CO²). Increasing light intensity, when managed properly, can promote optimal plant development and higher yields by enhancing photosynthesis and encouraging more robust growth.
Further Reading: Diagnosing And Fixing Light Burn In Cannabis Plants
Timing also matters. Photosensitive weed plants need:
In vegetation: 18-24 hours of light daily to keep growing
In flowering: 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness to initiate bud production
The light cycle is crucial for regulating the vegetative stage and triggering flowering, as adjusting light and dark periods directly influences plant development and yield. Even a brief light leak during the dark cycle can delay flowering or stress your plant.
Further Reading: Five Need-To-Know Formulas For Lighting A Grow Room

The Role of CO², Water, and Environment
Photosynthesis doesn’t happen with light alone. Your weed plants also need:
Carbon dioxide – used during the Calvin cycle to make sugars. With higher light intensity, plants benefit from added CO² (1200-1500 ppm in sealed rooms).
Water – Split during the light reactions to provide hydrogen for sugars and oxygen as a byproduct.
Temperature – Ideal is around 24-30°C during the day. If it gets too hot, photosynthesis slows or even shuts down. High temperatures above 30°C can impair enzyme function and reduce photosynthesis efficiency, so maintaining proper temperature is key for plant health.
Humidity and Airflow – Good airflow helps your plant breathe (transpire), moving water and nutrient from roots to leaves.
A 2008 study found that CO² enrichment in cannabis increased photosynthesis and overall biomass, especially when paired with strong lighting.
The Role of Carbon Dioxide in Cannabis Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide is more than just a background gas in your grow room—it’s an essential ingredient in the recipe for robust cannabis growth. During photosynthesis, weed plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air through tiny pores in their leaves called stomata. Once inside the plant, CO² becomes a key player in the process that transforms light energy into the sugars and oxygen that fuel plant growth and development.
For cannabis cultivation, maintaining the right carbon dioxide levels can make a dramatic difference. Under optimal conditions, with light intensity and temperature dialed in, increasing CO² concentrations to between 1,200 and 1,500 ppm can supercharge photosynthesis, leading to faster weed plant growth, thicker stems, and more impressive bud production. Some advanced growers even experiment with slightly higher levels, but it’s important to strike a balance—too much CO² without enough light or the right temperature can actually slow down the process.
Indoor growers have the unique advantage of being able to supplement carbon dioxide directly, using tanks, generators, or dissolvable tabs in the soil. This boost is especially effective when paired with strong lighting and stable temperatures, creating optimal conditions for cannabis photosynthesis. The result? Healthier weed plants, bigger yields, and a more efficient production cycle from seedling to harvest.
For any grower aiming to maximize the potential of their weed plants, understanding and managing carbon dioxide is just as essential as providing enough light or water. When all these elements work together, your weed plants can truly thrive.
How Photosynthesis Affects Weed Plant Yields and Cannabinoids

Why does all this matter to growers? Because how efficiently your weed plant uses light directly affects:
- Bud size and density
- Trichome production
- THC and CBD levels
- Flavour and aroma profiles
In short, if photosynthesis is running at full throttle, your cannabis plant isn’t just surviving – it’s thriving, producing more energy that can be used to boost cannabinoid and terpene synthesis, and gearing up to provide you with a higher quality of weed.
Studies in Plants and Horticulturae journals confirm that optimising light and environmental conditions improves not only yield but cannabinoid and terpene content as well. Yield and potency are often measured by the dry weight of the harvested flowers, which standardizes results by removing moisture and allows for accurate comparison of cannabinoid content between different growing conditions.
In summary, marijuana, the cultivated form of the cannabis plant, relies on efficient photosynthesis to maximize quality, potency, and overall yield.
Grow Lights: Choosing the Best Artificial Sun for Your Weed Plant
When growing cannabis indoors, your choice of grow lights can make or break your harvest. Since cannabis plants rely on light energy to drive photosynthesis, providing the right type and amount of light is essential for optimal plant growth, vigorous vegetative development, and abundant flowering.
LED lighting systems have become a favorite among indoor growers, thanks to their energy efficiency and the ability to fine-tune the light spectrum to match the needs of cannabis sativa and other cultivars. These lights can deliver the precise photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) that cannabis plants crave, ensuring that every leaf receives enough light for maximum photosynthetic response. With adjustable spectrum options, LEDs can provide more blue spectrum light during the vegetative phase and shift to a red-heavy spectrum for the flowering stage, supporting both lush growth and explosive bud production.

High-pressure sodium (HPS) lights are another popular choice, especially during the flowering stage. Their strong red spectrum light is known to boost bud size and density, making them a staple in many professional cannabis cultivation setups. However, HPS lights can generate more heat, so growers need to monitor air temperature and ensure proper ventilation to maintain optimal conditions.
When selecting grow lights, consider not just the type of light, but also the intensity (measured in PPFD), the quality of the spectrum, and the specific needs of your cannabis plants. Matching the light source to your plant’s stage of development—whether you’re encouraging vegetative growth or pushing for maximum flowering—will help you get the most out of your crop. For home growers and commercial cultivators alike, investing in the right lighting system is one of the most important steps toward achieving higher yields, better cannabinoid production, and truly exceptional cannabis.
Further Reading: LED vs HPS Lights: Which Are Best For Growing Cannabis
Helping your Weed Plant Soak it all in
Here’s how to get the most out of your light – and your plant:
- Use full-spectrum lighting or sunlight
- Match spectrum to plant stage (blue for veg, red for bloom)
- Monitor PPFD with a meter – don’t guess
- Ensure even light coverage across the canopy
- Increase CO² only when everything else is dialled in
- Maintain proper temperature and humidity
- Keep the dark period completely dark during flowering
Cannabis cultivators can leverage environmental control strategies, such as adjusting light intensity and temperature, to optimize photosynthesis and maximixe yield. Research from environmental sciences highlights the critical role of light and environmental management in enhancing cannabinoid production and overall plant health.
The more efficient the photosynthesis, the bigger and better the harvest.
Light is the Life Force of Weed Plants
Light isn’t just something your weed plant likes – it’s what makes its entire life possible. Like other plants, cannabis relies on photosynthesis to convert light into energy and drive growth. Through photosynthesis, cannabis turns air, water, and light into biomass, trichomes, and the precious compounds that make your weed plant what it is.
Understanding the science behind how a weed plant uses light helps you fine-tune your grow and take control of your results. When photosynthesis runs smoothly, your plants flourish and your buds shine.
So next time you flip on your grow light or see your outdoor garden basking in the sun, know that something miraculousi is happening in every leaf. Light is life. And when used wisely, it’s the secret to growing the best weed plants possible.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
References
Rodriguez-Morrison, E. et al. (2019). Lighting strategies affect morphology and cannabinoid content in Cannabis. Frontiers in Plant Science
Chandra, S. et al. (2008). CO₂ enrichment impacts on photosynthesis in Cannabis sativa. PubMed
Massa, G.D. et al. (2008). Light-emitting diodes in plant production. HortScience
Westmoreland, F. et al. (2021). PPFD thresholds for high-yield cannabis flowering. PubMed
Ahsan et al. Illuminating Cannabis sativa L.: The Power of Light in Enhancing C. sativa Growth and Secondary Metabolite Production Pubmed


