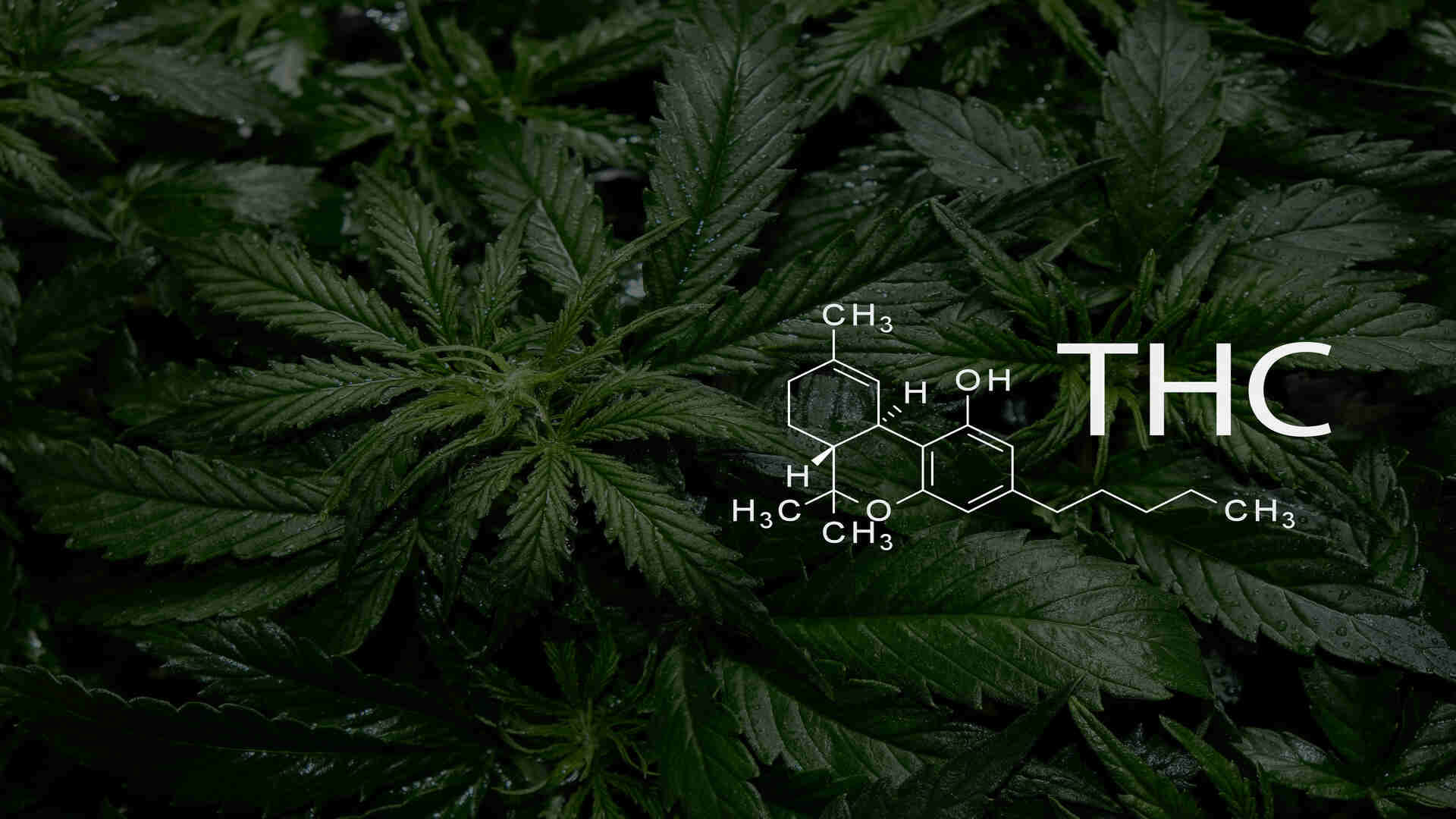
If you've used cannabis before, you'll be no stranger to Delta-9 THC. But what of its close deravitives, Delta-8 and Delta-10? And how much do you know about Delta-9 THC? The landscape of cannabis research has significantly expanded with the advent of different cannabinoids, each presenting unique effects and benefits. Among these cannabinoids, Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-8 THC), Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-9 THC), and Delta-10-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-10 THC) have gained considerable attention. Here, we take a simple look into what can sometimes be a heavy topic, inspecting some of the distinctions key between these three compounds, exploring how the body metabolizes them, and analyzing their respective effects on the human body and brain.
What Is THC?
First up, we have to look at what THC is. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis plants. It’s the chemical responsible for most of marijuana’s psychological effects, giving users that characteristic “high.” THC works by mimicking the actions of anandamide, a neurotransmitter naturally produced by the body. It binds to cannabinoid receptors, particularly in the brain, affecting areas responsible for memory, pleasure, coordination, and time perception. The following diagram illustrates the human endocannabinoid system:
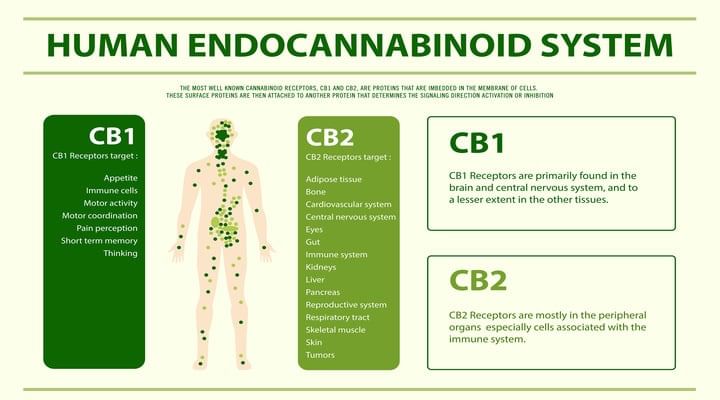
When consumed, THC can induce a range of effects, from euphoria and relaxation to altered sensory perception and increased appetite, or as we like to call it, "the munchies". However, its impact can vary based on the individual, dosage, and method of consumption.
Beyond recreational use, THC has medicinal applications. It’s used to alleviate pain, nausea (especially in chemotherapy patients), muscle spasticity, and insomnia. THC is usually consumed by smoking or vaporizing cannabis, but it can also be found in edibles, oils, and tinctures. The legal status of THC varies globally, with some places allowing medical use, recreational use, or both, while others maintain strict prohibitions.
Chemical Structure and Differences
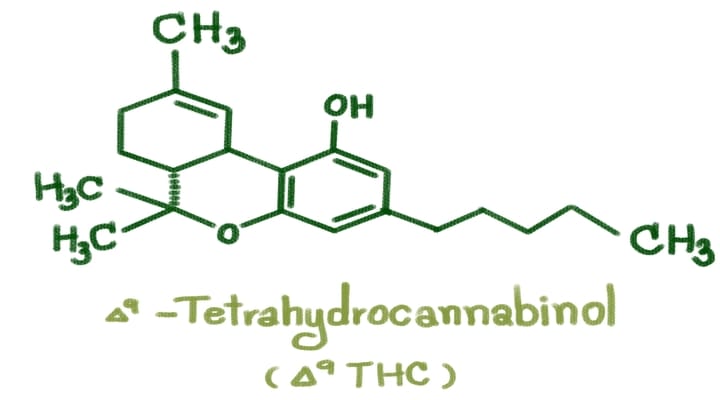
Delta-8, Delta-9, and Delta-10 THC are isomers, meaning they share the same molecular formula (C21H30O2) but differ in the placement of a double bond within their molecular structure. This seemingly minor variation significantly influences their pharmacological properties, or to put it simply, how they may affect you.
Delta-8 THC: This compound has the double bond on the eighth carbon atom, making it slightly different structurally from Delta-9.
Delta-9 THC: The most well-known and abundant cannabinoid in cannabis. The double bond is located on the ninth carbon atom of the chain.
Delta-10 THC: Here, the double bond is found on the tenth carbon atom, adding another layer of distinction.
Biosynthesis and Metabolism
The biosynthesis of these cannabinoids in the plant and their metabolism in the human body follow intricate pathways.
Biosynthesis in the Cannabis Plant
In cannabis plants, cannabinoids are produced through the decarboxylation of cannabinoid acids. THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is the precursor to Delta-9 THC, and it is synthesized in the plant from CBGA (cannabigerolic acid). Delta-8 and Delta-10 THC are generally found in much lower concentrations and are often produced through chemical conversion from Delta-9 THC or CBD.
Metabolism in the Human Body
Upon consumption, the metabolism of these cannabinoids involves several steps:
- Absorption: Whether ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, these cannabinoids enter the bloodstream.
- Distribution: They are distributed to tissues with high fat content, including the brain, where they exert their effects.
- Metabolism: Predominantly occurring in the liver, cannabinoids are metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4. Delta-9 THC is metabolized into 11-hydroxy-THC, a compound more potent than Delta-9 THC itself, before being further broken down into THC-COOH.
- Excretion: The metabolites are eventually excreted through urine and feces.
Pharmacodynamics: Effects on the Body and Brain
The interaction of these cannabinoids with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS) determines their effects. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), endogenous cannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of these endogenous compounds.
Delta-8 THC
- Receptor Affinity: Delta-8 THC also binds to CB1 receptors but with less affinity compared to Delta-9 THC. This difference results in a milder psychoactive effect.
- Effects: Delta-8 THC is often reported to produce a more clear-headed and less anxious high than Delta-9 THC. Users may experience mild euphoria, relaxation, and pain relief without the intense psychoactivity
Delta-9 THC
- Receptor Affinity: Delta-9 THC has a high affinity for CB1 receptors, predominantly found in the brain and central nervous system. This binding leads to the classic psychoactive effects associated with cannabis, such as euphoria, altered perception, and cognitive impairment.
- Effects: Common effects include euphoria, relaxation, altered sensory perception, increased appetite, and impaired memory and coordination. Delta-9 THC's psychoactivity can also lead to anxiety and paranoia in some users.
Delta-10 THC
- Receptor Affinity: Delta-10 THC binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors but with lower affinity compared to Delta-9 THC. This unique interaction profile may contribute to its distinct effects.
- Effects: Anecdotal reports suggest that Delta-10 THC provides a more energizing and less sedative experience. It is often described as more uplifting and mentally stimulating than both Delta-8 and Delta-9 THC .
Comparative Table
Characteristic | Delta-8 THC | Delta-9 THC | Delta-10 THC |
Chemical Structure | Double bond on 8th carbon | Double bond on 9th carbon | Double bond on 10th carbon |
Natural Abundance | Low | High | Low |
Psychoactivity | Mild | High | Mild to Moderate |
Receptor Affinity | Lower CB1 affinity | High CB1 affinity | Lower CB1 and CB2 affinity |
Common Effects | Clear-headed high, relaxation | Euphoria, altered perception | Uplifting, mentally stimulating |
Anxiety/Paranoia Risk | Lower | Higher | Lower |
Therapeutic Potential and Legal Status
The therapeutic potential and legal status of these cannabinoids vary significantly, and as always, you should check your local laws before obtaining or consuming THC products..
Delta-8 THC
- Therapeutic Uses: Emerging research suggests potential benefits in pain relief, anxiety reduction, and neuroprotection. However, more clinical studies are needed to fully understand its therapeutic profile .
- Legal Status: The legal status of Delta-8 THC is complex and varies by jurisdiction. It is often considered a legal gray area, as it can be derived from hemp, which is federally legal in the USA under the 2018 Farm Bill.
Delta-9 THC
- Therapeutic Uses: Delta-9 THC is well-studied for its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antiemetic, and appetite-stimulating properties. It is used in the treatment of chronic pain, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, and appetite loss in HIV/AIDS patients .
- Legal Status: Delta-9 THC remains a Schedule I controlled substance under federal law in the United States, although its medical use is legal in many states.
Delta-10 THC
- Therapeutic Uses: Due to its recent emergence, there is limited research on Delta-10 THC. Preliminary findings indicate possible uses in mood enhancement and focus improvement, but comprehensive studies are lacking.
- Legal Status: Similar to Delta-8, the legal status of Delta-10 THC is ambiguous and subject to interpretation of state and federal laws regarding hemp-derived cannabinoids.
Conclusion
Delta-8, Delta-9, and Delta-10 THC each offer unique profiles in terms of chemical structure, metabolism, and effects on the human body and brain. Delta-9 THC remains the most psychoactive and widely studied, with significant therapeutic applications but also higher risks of anxiety and legal restrictions. Delta-8 THC provides a milder psychoactive experience and potential therapeutic benefits, while Delta-10 THC is emerging as a cannabinoid with distinct, stimulating effects. Continued research is essential to fully elucidate the pharmacological properties and therapeutic potentials of these cannabinoids, guiding informed medical and recreational use.
Shop For HIgh-THC Strains on Seedsman
References
- Mechoulam, R., & Parker, L. A. (2013). The endocannabinoid system and the brain. Annual Review of Psychology, 64(1), 21-47. PubMed
- Pertwee, R. G. (2008). The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol, and Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. British Journal of Pharmacology, 153(2), 199-215. PubMed
- Baram, L., Peled, E., Berman, P., Yellin, B., & Besser, E. (2019). The heterogeneity and complexity of cannabis extracts as antitumor agents. Oncotarget, 10(24), 2205-2217. PubMed
- De Luca, M. A., Castelli, M. P., Loi, B., Porcu, A., Martorelli, M., Miliano, C., ... & Solinas, M. (2020). Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol in Cannabis and Cannabis-Based Medicines: Literature Review and Findings from a Recent Italian Study. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 5(1), 50-60. PubMed
- Gertsch, J., Pertwee, R. G., & Di Marzo, V. (2010). Phytocannabinoids beyond the Cannabis plant – do they exist? British Journal of Pharmacology, 160(3), 523-529. PubMed
- Abrams, D. I., Couey, P., Shade