Introduction
Understanding the medical vs. homegrown cannabis difference has become increasingly important as cannabis legalization spreads across the United States. With more states permitting both medical marijuana programs and home cultivation, consumers face essential choices about their cannabis source, including the distinction between medical and recreational marijuana. The quality, consistency, and legality of cannabis can vary significantly between professionally grown medical cannabis and homegrown varieties.
As a cultivation expert with more than 40 years of experience, I’ve observed the evolution of both medical and home cannabis production. This comprehensive guide examines the differences between medical-grade cannabis from dispensaries and homegrown cannabis from personal gardens. You’ll discover how these sources compare in quality, potency, safety, and value.
Whether you’re a medical cannabis patient seeking reliable medication or a home grower interested in producing your own supply, this comparison will help you make informed decisions about your cannabis options.

Understanding Medical Grade Cannabis
Medical-grade cannabis refers to cannabis grown, processed, and distributed through licensed dispensaries specifically for therapeutic use. Medical marijuana patients benefit from these rigorous quality control measures, ensuring they receive consistent potency, purity, and safety. This cannabis undergoes rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistent cannabinoid profile, purity, and safety for medical patients. While dispensaries do sell medical cannabis, not all dispensary cannabis is medical grade, particularly in states with recreational markets.
What Defines Medical Cannabis? Understanding Quality Standards and GACP Requirements
Medical cannabis is cannabis cultivated and processed under strict regulations for therapeutic purposes. Unlike recreational marijuana, medical cannabis is often prescribed by healthcare professionals for specific conditions like chronic pain, epilepsy, cystic fibrosis, multiple sclerosis, and cancer symptoms.
Regulatory Framework
The definition of medical cannabis varies by state. However, most states with medical marijuana programs require:
- Cultivation in licensed facilities
- Regular testing by certified laboratories
- Proper packaging with accurate labelling
- Distribution through regulated dispensaries
- Purchase only with a valid medical marijuana card
Medical cannabis patients may receive recommendations from physicians for medical marijuana, specific strains, cannabinoid ratios, and dosing protocols. Medical dispensaries operate under regulations that ensure products meet safety standards and contain accurate cannabinoid profiles for treating various medical conditions.
"The key distinction of medical cannabis is the regulatory framework surrounding its production and distribution," explains Dr. Ethan Russo, neurologist and cannabis researcher. "This oversight aims to provide patients with reliable, consistent medicine."
Good Agricultural and Collection Practices (GACP)
A critical component of medical cannabis quality begins at cultivation. The World Health Organization (WHO) has established Good Agricultural and Collection Practices (GACP) for medicinal plants – guidelines increasingly being adapted for cannabis production. These guidelines ensure that medicinal plants are grown, harvested, and processed in ways that preserve their therapeutic properties while minimizing contamination risks.
GACP requirements for medicinal cannabis typically include:
Seed and Propagation Material Selection: Using verified genetics with documented origins
Cultivation Environment Control: Maintaining optimal growing conditions with minimal contamination risks
Soil and Water Management: Testing for heavy metals and other contaminants
Pest Management: Following integrated pest management practices that minimize chemical use
Harvest Timing and Methods: Harvesting at optimal cannabinoid expression with contamination prevention
Post-Harvest Processing: Proper drying, curing, and storage to prevent microbial growth
Documentation: Comprehensive record-keeping throughout the cultivation and processing cycle
These GACP standards form the foundation for consistent, high-quality medical cannabis production before products even reach testing laboratories.
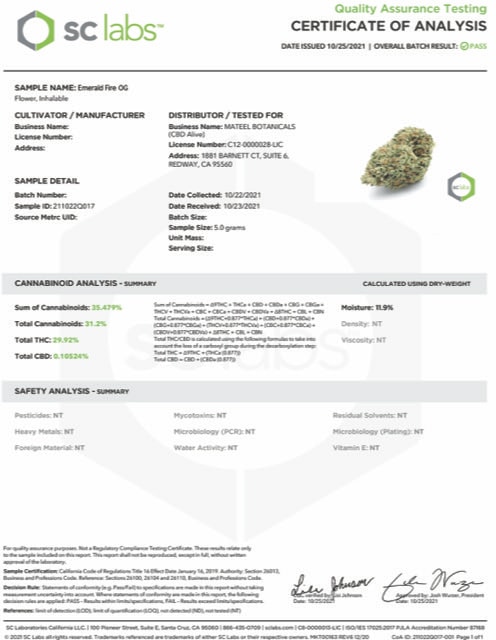
Quality Control and Lab Testing
The most significant advantage of medical-grade cannabis is consistent quality ensured through laboratory testing. While homegrown cannabis may undergo voluntary testing, medical dispensaries must comply with mandatory testing requirements.
Medical cannabis testing typically includes:
- Cannabinoid profiling - Measuring THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids
- Terpene analysis - Identifying aromatic compounds that influence effects
- Microbial screening - Testing for mold, yeast, and bacteria
- Pesticide testing - Checking for harmful pesticides
- Heavy metal testing - Detecting toxic metals like lead or arsenic
- Residual solvent testing - For concentrated products
These tests ensure patients receive cannabis free from harmful contaminants while providing accurate information about potency and composition. Medical dispensaries sell cannabis with detailed certificates of analysis, allowing consumers to verify exactly what they're purchasing.
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) certification represents the highest standard for pharmaceutical-grade cannabis. While not all medical cannabis achieves this standard, the industry increasingly adopts these rigorous quality control protocols, building upon the foundation established by GACP implementation.
By following GACP guidelines throughout cultivation and processing and then verifying quality through comprehensive lab testing, medical cannabis producers create a continuous quality assurance system that delivers safe, consistent medicine to patients.
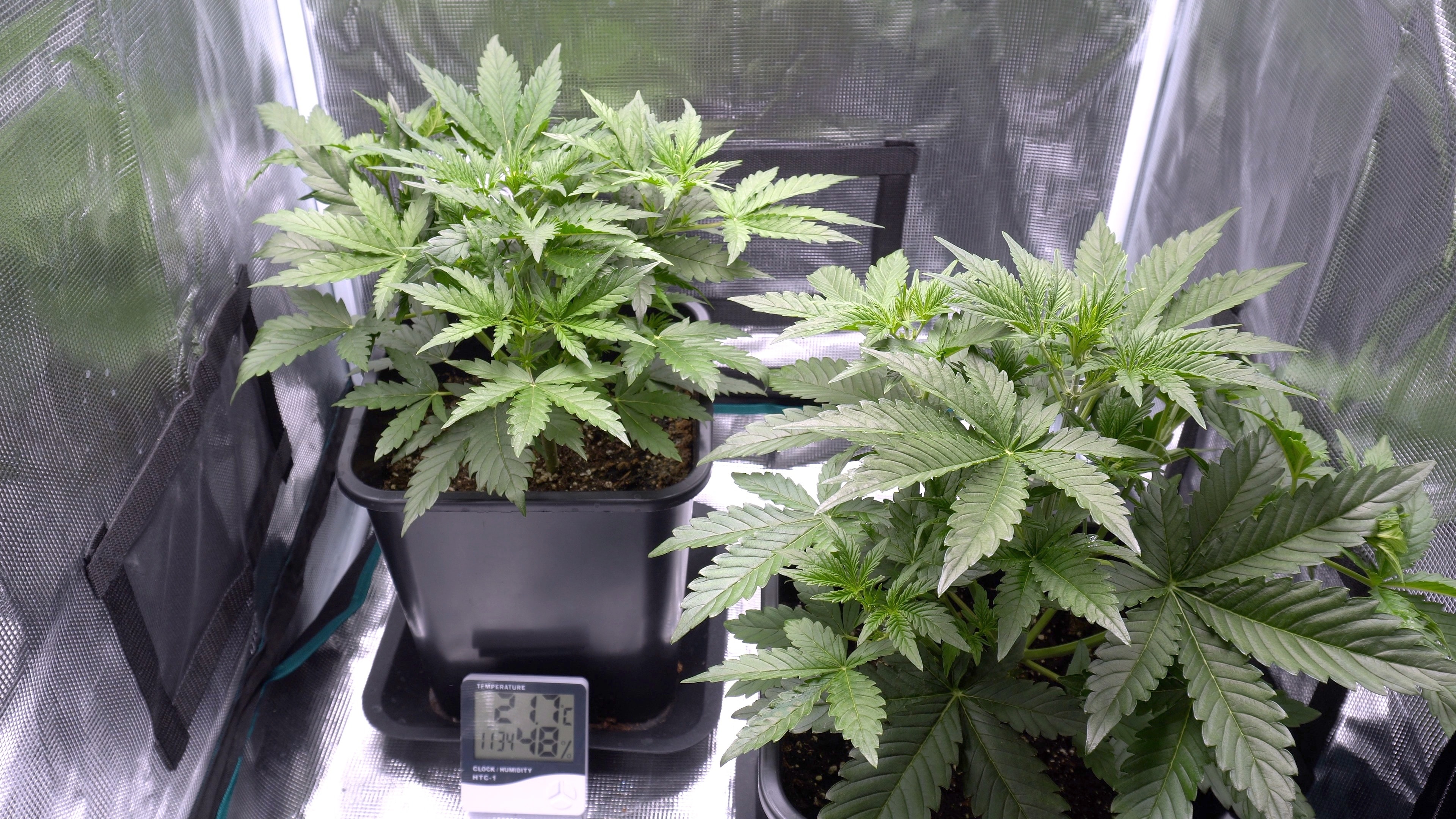
The Homegrown Cannabis Experience
Growing cannabis at home offers a unique experience that differs significantly from purchasing at dispensaries. However, when you grow cannabis at home, you must consider challenges such as legal regulations and space requirements. Home cultivation allows personal connection to the plant and complete control of growing methods.
Benefits of Growing Your Own Cannabis
Growing your cannabis provides several advantages that appeal to both medical patients and recreational marijuana users:
Complete Control Over Growing Methods
Home indoor growers determine every aspect of cultivation, including:
- Growing medium (soil, hydroponic, etc.)
- Nutrient programs
- Grow lights and photoperiod
- Organic or chemical-based approaches
- Harvest timing
This control allows cultivators to produce cannabis tailored to personal preferences. Many home gardeners grow organically. This DIY cannabis-growing approach often results in products grown with greater care than mass-produced alternatives.
Potential Cost Savings
While home growing requires initial investment, it typically becomes cost-effective after a crop or two:
Expense Category | Homegrown (Annual) | Dispensary (Annual) |
Initial Setup | $500-1,500 | $0 |
Seeds/Clones | $50-200 | $0 |
Growing Supplies | $300-600 | $0 |
Electricity | $300-1,200 | $0 |
Product Cost | $0 | $2,400-7,200 |
Total | $1,150-3,500 | $2,400-7,200 |
This cost analysis is based on the typical consumption of 1-2 grams daily at average dispensary prices of $8-20 per gram.
Personal cannabis grow operations can yield significant savings, especially for regular consumers. After covering startup costs, every subsequent harvest will cost less than the first.
Personal Connection and Satisfaction
Many home growers are super satisfied when they grow their own cannabis plants. Growing your own gives growers a meaningful relationship with the plant and a deeper appreciation for the final product.
“There’s something special about consuming cannabis you’ve grown yourself,” says Jorge Cervantes, renowned cannabis cultivation expert. “You are able to develop an intimate understanding of the plant’s needs and characteristics that deepens your appreciation for the end result.”

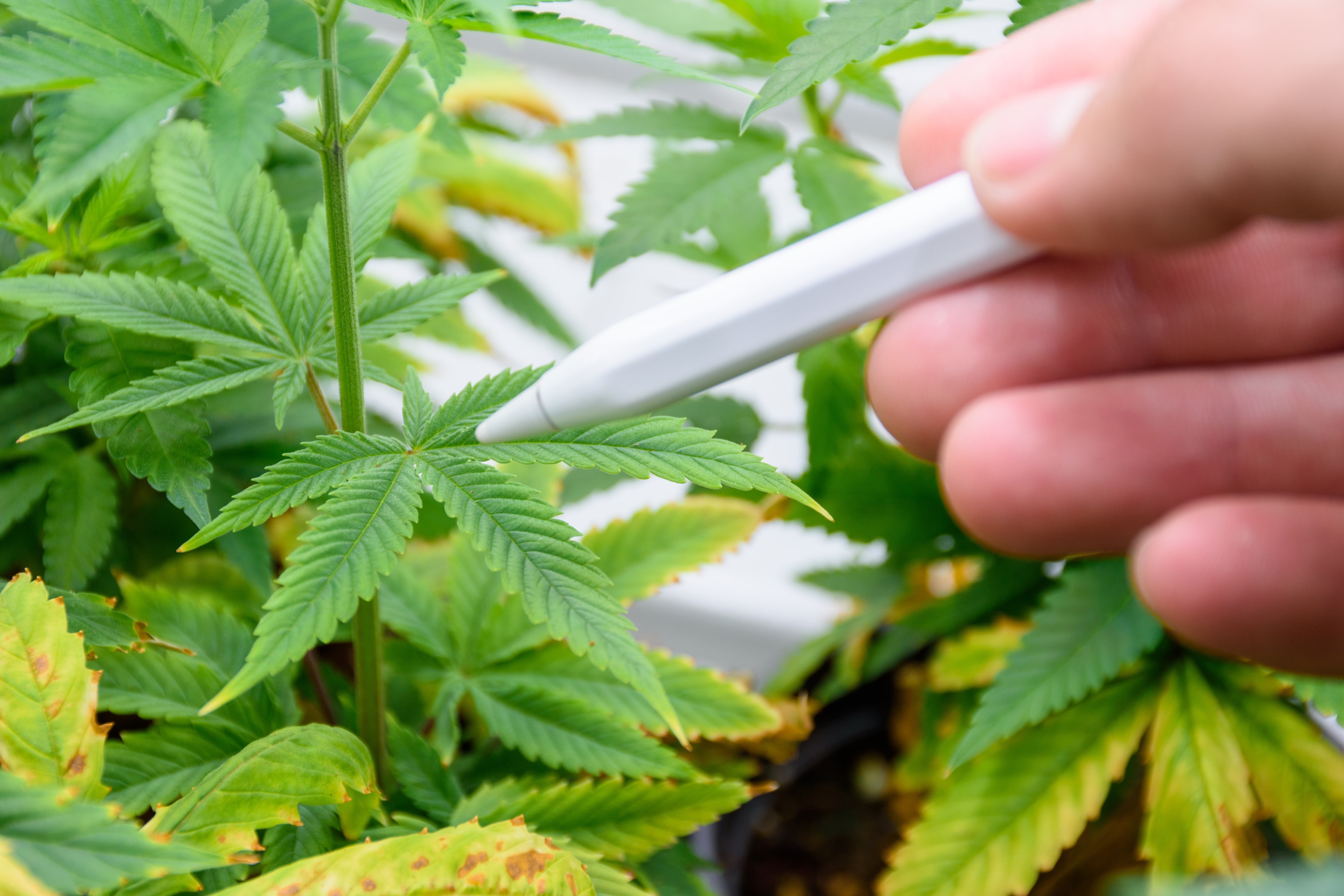
Challenges of Home Cannabis Cultivation
Despite its rewards, home growing presents several challenges:
Knowledge and Experience Requirements
Successful cannabis cultivation demands understanding:
- Plant biology and life cycles
- Nutrient requirements
- Pest and disease management
- Proper harvesting, drying, and curing methods
The learning curve can be steep for beginners. Growing high-quality cannabis requires study and practice, with many first-time growers experiencing disappointing results.
Space and Equipment Needs
Home cultivation requires:
- Dedicated growing space
- Proper lighting (HID, LED, or natural sunlight)
- Air ventilation systems
- Temperature and humidity control
- Nutrients and growing medium
These requirements may prove challenging in limited living spaces. Outdoor cultivation offers more space but faces weather limitations, security issues, and seasonal restrictions.
Consistency Challenges
Even experienced home growers struggle with consistency between harvests. Variables including environmental fluctuations, genetic variations, and cultivation techniques cause differences in:
- Potency
- Terpene profiles
- Yield
- Overall quality
Achieving consistent results requires precise record-keeping and controlled growing environments.

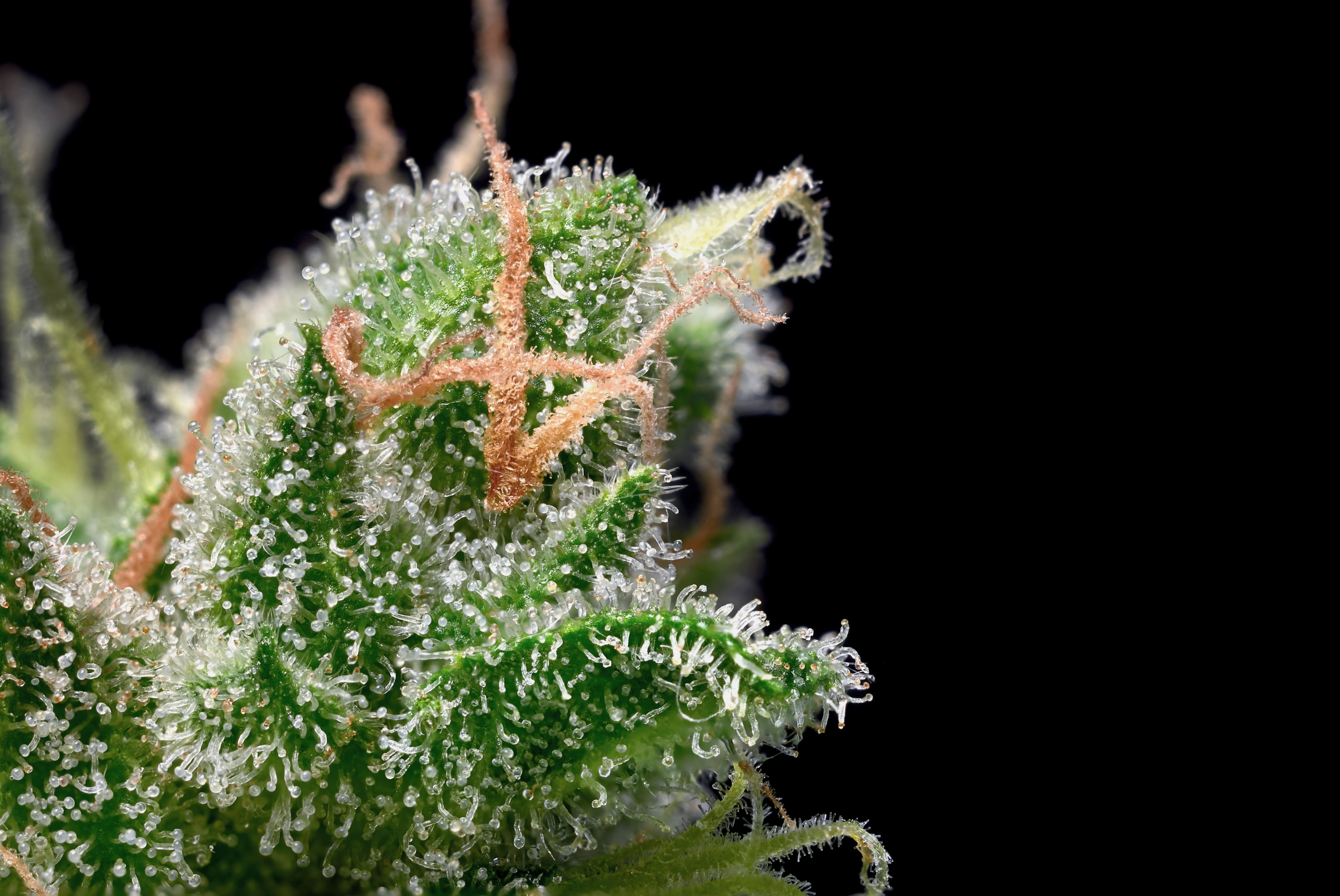
Key Differences in Quality and Safety
When comparing medical vs. homegrown cannabis, quality and safety represent critical considerations. Several factors influence the quality of cannabis from both sources.
Cannabinoid and Terpene Profiles
Potency Consistency
Medical cannabis maintains consistent potency through standardized growing conditions and genetic selection. Dispensaries sell products with clearly labeled THC and CBD percentages, allowing patients to select appropriate potency levels and terpene qualities.
Homegrown cannabis potency can vary significantly based on:
- Genetics
- Growing conditions
- Harvest timing
- Curing methods
The question, "Is homegrown stronger than dispensary?" has no simple answer. While professional growers can achieve high potency through optimized conditions, skilled home growers can match or exceed dispensary potency levels. However, novice growers often produce cannabis with lower or inconsistent potency compared to medical-grade alternatives.
Variety of Available Profiles
Medical dispensaries offer diverse cannabinoid and terpene profiles to address different medical conditions. Patients can select from:
- High-THC varieties for pain and nausea
- High-CBD options for anxiety and inflammation
- Balanced THC:CBD ratios for neurological conditions
- Specific terpene profiles for targeted effects
Home growers face limitations in seed and clone availability. While online seed banks offer numerous options, specific medicinal strains may prove challenging to acquire. Additionally, maintaining genetic stability requires advanced breeding knowledge.

Purity and Contamination Issues
Testing Capabilities
Medical cannabis undergoes mandatory testing for various contaminants. Professional laboratories use advanced equipment to detect:
- Pesticide residues (often to parts per billion)
- Microbial contamination
- Heavy metals
- Mycotoxins
- Growth regulators
Home growers rarely access such comprehensive testing. Consumer-level testing kits provide limited information about potency but typically cannot detect low-level contaminants. This testing gap represents a significant advantage for medical cannabis when safety is paramount.
Common Contaminants
Both medical and homegrown cannabis face contamination risks, though from different sources:
Medical cannabis contamination risks:
- Approved pesticides used incorrectly
- Cross-contamination in processing facilities
- Storage contaminants
- Treatment chemicals exceeding limits
Homegrown cannabis contamination risks:
- Mold and mildew
- Household pesticides unsafe for consumption
- Environmental pollutants in soil or water
- Pest infestations
Professional operations implement strict contamination prevention protocols. Home growers must exercise vigilance but may lack sophisticated detection methods.
Is homegrown weed better for you? When grown organically without harmful chemicals, homegrown cannabis can offer purity advantages over some commercial operations. However, without testing, undetected contaminants remain a concern.

Legal Considerations and Accessibility
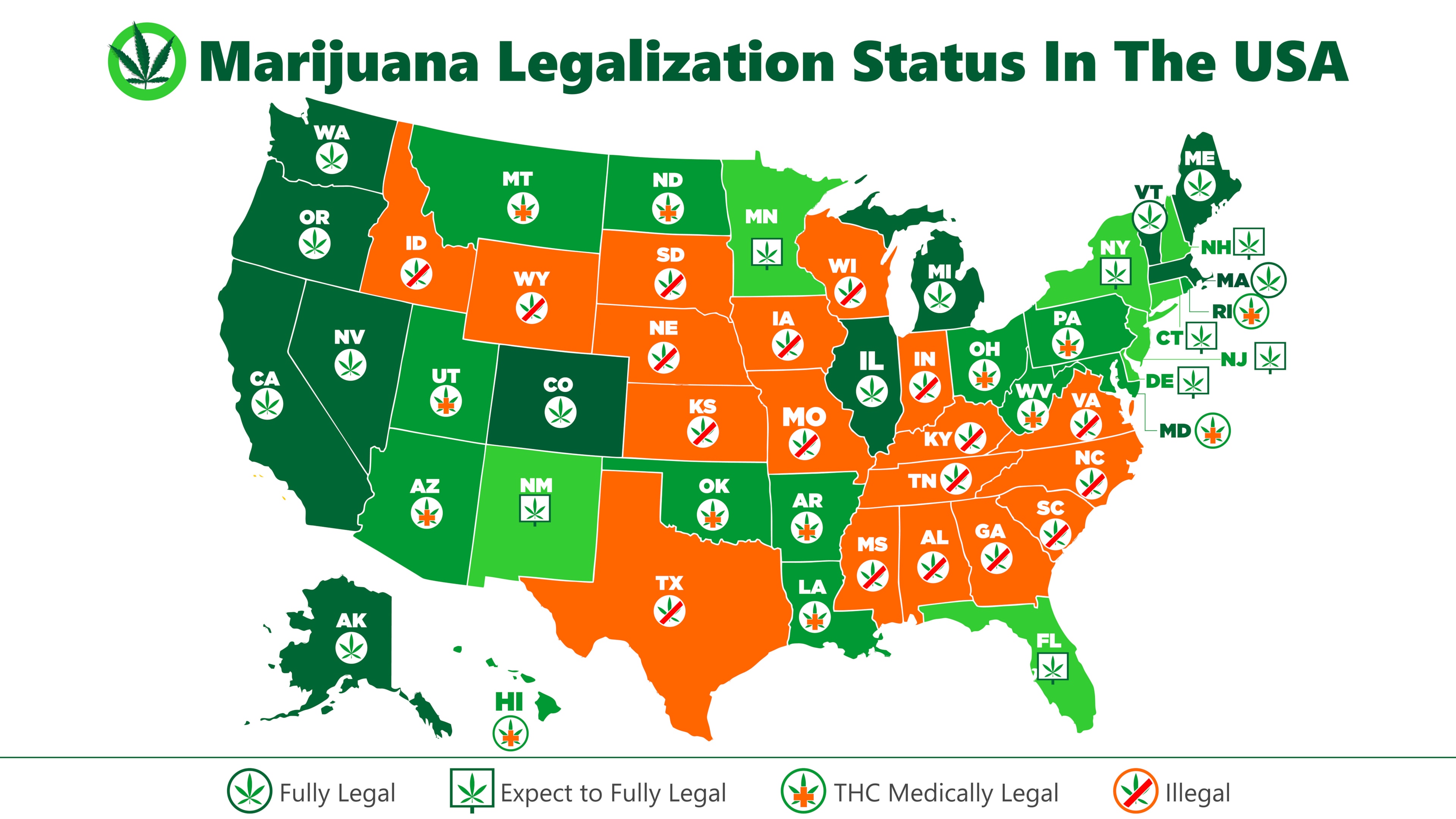
The legal status of cannabis varies dramatically across the United States, creating a complex landscape for both medical cannabis and home cultivation.
State-by-State Regulations
Cannabis remains federally illegal despite state-level legalization. States with legal cannabis have established varying regulations for medical programs and home cultivation.
Medical Cannabis Regulations
Medical marijuana programs operate in 37 states plus Washington, D.C. These programs feature:
- Patient registration requirements
- Qualifying condition lists
- Purchase limits
- Product restrictions
- Dispensary licensing procedures
Medical patients receive legal protections and access to products unavailable to recreational users in many states.
Home Growing Limits
How many marijuana plants can you grow in legal states? Limits vary significantly:
State | Medical Patient Limit | Recreational Limit |
California | 6 plants (more with doctor recommendation) | 6 plants |
Colorado | 6 plants (3 flowering) | 6 plants (3 flowering) |
Michigan | 12 plants | 12 plants |
Oregon | 6 plants | 4 plants |
Washington | 6 plants (15 with authorization) | No home growing |
Arizona | 12 plants (if >25 miles from dispensary) | 6 plants |
Many states prohibit home growing entirely, making dispensary access the only legal option. However, as regulations frequently change, verifying current local laws before beginning cultivation is important.
Access Considerations
Dispensary Convenience vs. Home Growing Commitment
Dispensary weed offers convenience that home growing cannot match:
- Immediate availability
- Professional guidance
- Product variety
- No cultivation knowledge required
However, dispensaries present barriers, including:
- Geographic limitations (dispensary deserts)
- Operating hours restrictions
- Supply shortages
- Higher costs
Home growing requires significant time commitment and patience. Plants typically take 3-4 months from seed to harvest, plus additional time for curing. This timeline makes home cultivation impractical for immediate needs.
Medical Marijuana Card Requirements
Medical marijuana cards provide several advantages:
- Legal protection in medical-only states
- Tax exemptions in some jurisdictions
- Higher possession limits
- Access to higher-potency products
- Potentially lower age requirements (18+ vs. 21+)
However, obtaining a card involves:
- Doctor consultations
- Application fees
- Annual renewal costs
- Privacy considerations
- Potential federal implications (firearm ownership, employment)
What are the disadvantages of a medical marijuana card? Beyond costs and privacy concerns, cardholders may face restrictions on driving, employment in specific sectors, and housing options. These factors require careful consideration when deciding between medical registration and home cultivation.

Cost Comparison Analysis
Financial considerations often influence decisions between dispensary purchases and home cultivation. Both options involve different cost structures worth examining.
Short-term vs Long-term Expenses
Initial Home Growing Investment
Starting a home cannabis grow requires upfront expenses:
Basic indoor setup (2-4 plants):
- Grow tent: $80-300
- Lighting: $100-500
- Ventilation: $50-200
- Growing medium: $30-100
- Nutrients: $50-150
- Seeds or clones: $30-200
- Miscellaneous supplies: $100-300
- Total: $440-1,750
Basic outdoor setup (2-4 plants):
- Seeds or clones: $30-200
- Soil and amendments: $50-150
- Container costs: $20-100
- Basic nutrients: $30-100
- Pest control: $20-80
- Total: $150-630
These initial investment figures vary based on quality, scale, and growing method. Hydroponic systems typically cost more initially but may produce higher yields.
Ongoing Expenses
Home growing involves recurring costs:
- Electricity (indoor): $30-100 monthly
- Water: $5-20 monthly
- Nutrients: $10-50 monthly
- Growing medium replacement: $20-60 per cycle
- Seed/clone replacement: $30-200 per cycle
Dispensary purchases involve straightforward per-gram or per-ounce pricing:
- Average medical cannabis cost: $8-15 per gram
- Monthly supply (1g daily): $240-450
- Annual cost: $2,880-5,400
Home growing typically becomes cost-effective for regular consumers after 1-2 harvests, despite higher initial investment.
Value Considerations Beyond Price
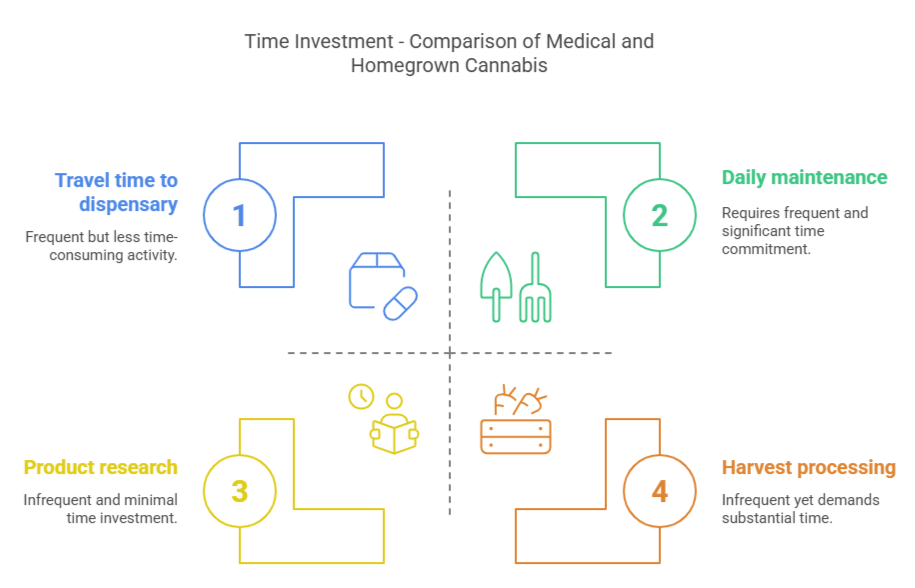
Time and Convenience Factors
When evaluating expenses, consider non-monetary costs:
Home growing time investment:
- Daily maintenance: 10-30 minutes
- Weekly major tasks: 1-3 hours
- Harvest processing: 8-20 hours per harvest
- Learning and troubleshooting: Variable
Dispensary time investment:
- Travel time to/from dispensary
- Wait time at dispensary
- Product research and selection
For busy individuals, the convenience of dispensary purchases may outweigh potential financial savings from home cultivation.
Quality and Consistency Value
Medical cannabis provides dosage accuracy and consistent potency that prove valuable for patients requiring precise medication. The ability to purchase identical products repeatedly represents a significant advantage for medical treatment protocols.
What is the downside of medicinal cannabis? Beyond higher costs, potential downsides include:
- Limited strain availability in some markets
- Inadequate testing in poorly regulated states
- Patient privacy concerns
- Accessibility challenges in rural areas
For recreational users and patients with less stringent needs, these factors may prove less important than cost savings from home growing.

Is Homegrown Cannabis as Good as Medical?
This question represents one of the most common comparisons between medical and homegrown cannabis. The answer depends on multiple factors and individual priorities.
When comparing medical and recreational marijuana, it's important to note that medical marijuana is often subject to stricter quality controls and production processes to ensure it meets medical standards. In contrast, recreational marijuana may have different quality and production standards.
Comparing Overall Quality Factors
When evaluating cannabis quality, consider several criteria:
Potency and Consistency
Medical cannabis typically offers:
- Verified potency through testing
- Batch-to-batch consistency
- Detailed cannabinoid profiles
- Specific THC:CBD ratios
Homegrown cannabis varies in consistency, and quality is heavily dependent on grower expertise, genetics, and growing conditions. Experienced home growers can produce cannabis that matches or exceeds dispensary quality, while beginners typically produce lower-quality results.
Cultivation Methods and Inputs
Medical cultivation facilities utilize:
- Advanced growing technologies
- Controlled environments
- Standardized nutrients
- Integrated pest management
- Professional trimming and curing
Home growers employ diverse methods ranging from basic soil cultivation to sophisticated hydroponic systems. This diversity creates significant quality variation among homegrown products.
Is home grown weed better for you? When grown organically without synthetic pesticides, homegrown cannabis can offer advantages for health-conscious consumers concerned about chemical exposure.
Variety and Selection
Medical dispensaries provide:
- Diverse strain selection
- Multiple consumption methods
- Consistent availability
- Product innovation
Home growers face limitations in variety unless they maintain multiple strains simultaneously, which requires additional space and resources.

When Homegrown May Be Superior
Home cultivation offers distinct advantages in several scenarios:
Control Over Growing Methods
Home growers exercise complete control over:
- Organic vs. conventional methods
- Nutrient programs
- Flushing protocols
- Harvest timing
- Curing processes
This control allows cultivation tailored to personal preferences, potentially producing cannabis better suited to individual needs than standardized commercial products.
Freshness Advantages
Freshly harvested homegrown buds offer:
- Full terpene preservation
- Optimal moisture content
- No degradation from packaging and storage
- Harvest timing flexibility
Commercial cannabis often sits in storage and packaging for weeks or months before purchase, potentially losing aromatic compounds and freshness.
Custom Strain Selection
Home growers can select and maintain specific strains ideally suited to their personal needs, which is particularly beneficial for medical patients with unique symptom profiles. This customization may prove difficult through dispensaries with rotating or limited inventories.

When Medical Cannabis Offers Advantages
Medical cannabis provides significant benefits in certain circumstances:
Consistency and Reliability
For patients requiring consistent medication, medical cannabis offers:
- Verified cannabinoid content
- Batch-to-batch reliability
- Detailed product information
- Pharmacist consultation (in some states)
This consistency proves particularly important for medical conditions requiring precise dosing and predictable effects.
Professional Expertise and Equipment
Commercial operations utilize:
- Master growers with extensive experience
- State-of-the-art cultivation technology
- Advanced extraction equipment
- Professional quality control systems
These advantages create products that are difficult to replicate in home settings, particularly for concentrates and specialized formulations.
Special Medical Formulations
Medical dispensaries increasingly offer:
- Precise cannabinoid ratios
- Minor cannabinoid products (CBG, CBN, etc.)
- Targeted terpene profiles
- Pharmaceutical-grade preparation
- Specialized delivery methods
These advanced formulations target specific conditions with precision beyond most home cultivation capabilities.
What is considered medical-grade marijuana? The highest standard includes GMP certification, full-panel testing, standardized potency, and pharmaceutical preparation. This level of quality supports specific medical applications that require absolute consistency.

Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
With an understanding of the differences between medical and homegrown cannabis, you can make an informed decision based on your specific situation and priorities.
Factors to Consider
When choosing between medical cannabis and homegrown cannabis, evaluate the following considerations:
Medical Requirements
For patients with severe medical conditions, consider:
- Need for consistent dosing
- Requirement for specific cannabinoid ratios
- Importance of contaminant testing
- Necessity of professional guidance
Medical cannabis patients treating serious conditions like epilepsy, cancer, or autoimmune disorders generally benefit from the consistency and oversight of dispensary products.
Time and Resource Availability
Home cultivation requires:
- Dedicated growing space
- Regular maintenance time
- Willingness to learn cultivation techniques
- Patience through the growing cycle
Individuals with limited time, restricted living space, or frequent travel may find dispensary cannabis more practical despite higher costs.
Legal Considerations
Evaluate your local legal landscape:
- Medical program availability
- Home growing allowances
- Possession limits
- Employment consequences
- Housing restrictions
In some regions, legal considerations may effectively decide for you based on available options.

Hybrid Approaches
Many consumers find that combining approaches provides optimal results.
Supplementing Home Growing with Dispensary Purchases
Consider using dispensaries to:
- Fill gaps between harvests
- Access different consumption methods
- Try new strains before growing
- Obtain products difficult to produce at home
This hybrid approach leverages the economic benefits of home growing while maintaining access to commercial variety and convenience.
Learning from Professional Techniques
Improve your home cultivation by:
- Researching commercial growing methods
- Adopting appropriate professional techniques
- Networking with industry professionals
- Taking cultivation courses
Implementing professional knowledge can significantly enhance home-growing results, narrowing the quality gap in medical products.
Finding Your Optimal Balance
The ideal approach varies based on individual circumstances. Many find that starting with dispensary purchases while learning to grow provides a smooth transition to home cultivation. Others maintain small personal gardens while still utilizing dispensaries for specific products.

Expert Tips for Evaluating Cannabis Quality
Whether purchasing from dispensaries or evaluating your homegrown harvest, understanding quality indicators helps ensure an optimal experience.
Visual and Sensory Assessment
Appearance Indicators
Quality cannabis typically displays:
- Dense, well-formed buds
- Rich coloration (green with possible purple, orange, or red hues)
- Visible trichome coverage (crystalline appearance)
- Proper trim with minimal leaf material
- Natural bud structure without compression
Poor quality indicators include excessive stems, seeds, loose structure, and brown coloration.
Aroma Evaluation
The cannabis smell provides valuable quality information:
- A strong, distinct aroma indicates terpene preservation
- Musty or hay-like smells suggest improper drying/curing
- Chemical odors may indicate residual nutrients or pesticides
- Sweet, fruity, earthy, or spicy notes typically indicate proper ripeness and curing
What is considered high-potency marijuana? Cannabis with THC levels exceeding 20% is generally considered high-potency, though terpene content and other cannabinoids significantly influence effects beyond THC percentage alone.
Texture Assessment
Physical characteristics reveal proper cultivation and processing:
- Slightly springy bud structure (not too dry or too moist)
- Sticky resin feel without excessive moisture
- Stems that snap rather than bend
- Even consistency throughout the bud

Understanding Product Information
For dispensary products, understanding labels and test results enhances selection:
Reading Lab Test Results
Cannabis certificates of analysis provide:
- Cannabinoid percentages (THC, CBD, etc.)
- Terpene profiles and percentages
- Pass/fail results for contaminants
- Harvest and testing dates
Look for comprehensive testing from accredited laboratories, recognizing that higher THC percentages don't necessarily indicate superior quality.
Interpreting Cannabinoid Percentages
Understanding concentration helps predict effects:
- THC: Primary psychoactive component
- CBD: Non-intoxicating, potentially therapeutic
- Minor cannabinoids (CBG, CBN, CBC): Contribute to entourage effect
- THCA vs. THC: Raw vs. activated forms
What is the purest form of marijuana? What is purity of marijuana? Purity refers to cannabis free from contaminants rather than potency. The purest forms undergo extensive testing to verify freedom from pesticides, heavy metals, and microbial contamination, regardless of THC content.
Identifying Red Flags
Watch for warning signs of poor quality or potentially unsafe products:
- Missing or incomplete test results
- Unusually high THC percentages without verification
- Significant discrepancies between label and appearance
- Bargain pricing far below market rates
- Packaging without proper safety seals

Conclusion: Bridging the Gap Between Medical and Homegrown Cannabis
The medical vs. homegrown cannabis difference represents a spectrum rather than a simple binary comparison. Both sources can provide high-quality cannabis when adequately produced and evaluated.
Medical cannabis offers advantages in consistency, testing, variety, and convenience. These benefits prove particularly valuable for patients requiring precise medication and those unable or unwilling to invest time in cultivation. Professional operations' regulatory oversight and quality control systems provide assurance difficult to replicate at home.
Homegrown cannabis provides benefits in cost savings, cultivation control, and personal connection to the plant. For those with appropriate space, time, and interest, home cultivation offers a rewarding way to produce cannabis tailored to individual preferences. Many experienced home growers achieve quality that rivals or exceeds commercial products.
The ideal approach depends on your specific needs, resources, and priorities. Many consumers find that combining dispensary purchases with home growing provides optimal results, leveraging the strengths of each source.
As cannabis legalization continues to expand nationwide, medical and home cultivation options will likely become increasingly accessible. Staying informed about legal developments, cultivation techniques, and quality evaluation methods will help you navigate this evolving landscape successfully.
Whether you choose medical cannabis, homegrown varieties, or a combination approach, understanding the differences empowers you to make choices aligned with your personal needs and circumstances.

Top 5 Strains For Homegrow Beginners
Choosing the right strain is crucial for a successful homegrown cannabis experience, especially for beginners. Here are five strains that are known for their ease of growth, resilience, and rewarding yields:
Sour Diesel Auto: This popular strain is a favorite among novice growers due to its robust nature and high yield. With a moderate THC level of around 19%, is celebrated for its energizing and uplifting effects, making it a great choice for daytime use.
Buy Sour Diesel Auto Cannabis Seeds
Blueberry: Known for its hardy nature, Blueberry can thrive in various conditions, making it ideal for beginners. It boasts a moderate THC level of around 16% and is prized for its relaxing and calming effects, perfect for unwinding after a long day.
Northern Lights Auto: A classic strain that has stood the test of time, Northern Lights Auto is renowned for its ease of growth and generous yield. With a THC level of around 18%, it offers relaxing and sedating effects, making it a popular choice for evening use.
Buy Northern Lights Auto Cannabis Seeds
Green Crack Auto: Despite its intense name, Green Crack Auto is a beginner-friendly strain known for its vigorous growth and high yield. It has a moderate THC level of around 17% and provides energizing and uplifting effects, ideal for boosting creativity and focus.
Buy Green Crack Auto Cannabis Seeds
Dr Seedsman CBD 30:1: Dr Seedsman CBD 30:1 is an excellent choice for those interested in a CBD-rich strain. It is easy to grow and yields well, with a lower THC level of around 0-4%. Dr Seedsman 30:1 is often used for its relaxing and calming effects without the intense psychoactive high, making it suitable for medical cannabis patients.
Buy Dr Seedsman CBD 30:1 Cannabis Seeds
Convenience
When it comes to convenience, both homegrown weed and dispensary weed have their unique advantages. Dispensary weed offers the ultimate convenience of being able to purchase high-quality cannabis products at any time without the need to invest time and effort into growing and harvesting your own plants. This is particularly beneficial for those with busy lifestyles or limited space for cultivation.
On the other hand, homegrown weed can also be convenient in its own right. Growing your own cannabis allows you to have a steady supply of your favorite strains without relying on dispensaries. This approach can be especially advantageous during times of high demand or supply shortages at dispensaries. Additionally, home cultivation provides the satisfaction of knowing exactly how your cannabis was grown, including the ability to use organic methods and avoid synthetic pesticides.
Ultimately, the choice between homegrown and dispensary weed depends on your personal preferences, lifestyle, and the level of control you wish to have over your cannabis supply.
Medical Marijuana vs Recreational Cannabis
Medical marijuana and recreational cannabis serve different purposes and cater to various needs. Understanding the distinction between the two can help you make informed decisions about your cannabis use.
Medical marijuana is specifically used to treat a variety of medical conditions such as chronic pain, nausea, seizures, and more. Healthcare professionals often prescribe it, and it is available through licensed medical dispensaries. Medical marijuana typically has higher levels of CBD and lower levels of THC, as CBD is known for its therapeutic benefits without the psychoactive effects of THC.
Recreational cannabis, on the other hand, is used primarily for its psychoactive effects and is often consumed for relaxation and enjoyment. Recreational cannabis usually has higher levels of THC and lower levels of CBD, providing the euphoric and mind-altering effects that many users seek.
THC and CBD Levels
One of the main differences between medical marijuana and recreational cannabis lies in their THC and CBD levels. Medical marijuana often contains higher levels of CBD, which is effective in treating various medical conditions without causing significant psychoactive effects. Recreational cannabis, conversely, tends to have higher levels of THC, which is responsible for the “high” that users experience.
While medical marijuana is primarily used for its therapeutic benefits, recreational cannabis is enjoyed for its psychoactive effects. However, it’s important to note that both types of cannabis can have medicinal properties, and the distinction between them is not always clear-cut. The terms are often used interchangeably, but understanding the general differences can help you choose the right product for your needs.
By recognizing the unique characteristics and benefits of medical marijuana and recreational cannabis, you can make more informed decisions about your cannabis consumption, whether for therapeutic purposes or recreational enjoyment.
Author Bio
Jorge Cervantes is a world-renowned cannabis cultivation expert with over 40 years of experience. His books, including "The Cannabis Encyclopedia" and "Marijuana Horticulture: The Indoor/Outdoor Medical Grower's Bible," have helped millions of growers worldwide. Jorge has traveled extensively, studying cannabis cultivation techniques across six continents, and continues to share his knowledge through publications, videos, and educational resources.