Cannabis cultivation can be made quicker and easier if you grow autoflowering strains. Autoflower plants are favored for their rapid growth cycle, resilience, and ease of cultivation. However, understanding and managing their nutrient requirements throughout their lifecycle is crucial to maximize yield and potency.
This guide provides a breakdown of the nutrient needs of autoflowering cannabis plants, stage by stage, along with practical options and tips to ensure a successful grow. As always, remember that different strains may have slightly different needs, so be on the lookout for signs that your plant needs more or less nutrients, and be prepared to make small adjustments on the fly.
Introduction to Autoflowering Cannabis Nutrient Management
Autoflowering cannabis plants (Cannabis ruderalis hybrids) flower based on age rather than light cycle, typically completing their lifecycle in 8 to 12 weeks from seed to harvest. This rapid growth cycle of the autoflowering cannabis plant necessitates careful nutrient management to support vigorous development and high-quality yields.

Nutrient management involves providing the right balance of macro and micronutrients at each growth stage. Key macronutrients include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), while essential micronutrients include calcium, magnesium, iron, and others. Proper nutrient management ensures healthy growth, robust flowering, and optimal resin production.
Seedling Stage (Week 1-2)

Nutrient Needs
During the seedling stage, autoflowering cannabis plants are delicate and require minimal nutrients. The primary focus is on establishing a strong root system and healthy initial growth.
Macronutrients: Very low levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Micronutrients: Trace amounts of calcium, magnesium, and iron.
As the plants transition from the seedling stage to the vegetative phase, it is crucial to adjust nutrient levels to support robust growth.
Nutrient Options
Plain Water: Initially, use plain, pH-balanced water (pH 6.0-6.5) to avoid nutrient burn. It's crucial to avoid overwatering, as seedlings are particularly susceptible to root rot.
Mild Seedling Fertilizer: If necessary, use a diluted seedling-specific fertilizer (1/4 strength of recommended dosage) to provide a gentle nutrient boost.
Vegetative Stage (Week 3-4)

Nutrient Needs
As the plant enters the vegetative stage, its growth rate accelerates, and the demand for nutrients increases. Nitrogen becomes particularly important for leaf and stem development.
Macronutrients: Higher levels of nitrogen, moderate phosphorus, and potassium.
Micronutrients: Continued supply of calcium, magnesium, and iron.
Unlike photoperiod plants, autoflowers do not rely on specific light cycles to initiate flowering, which can affect their nutrient needs.
Nutrient Options
Vegetative Fertilizer: Use a balanced N-P-K ratio fertilizer such as 3-1-2 or 4-2-3.
Organic Options: Organic growers can use compost teas, worm castings, or fish emulsion to provide a natural nutrient source. Liquid seaweed and kelp extracts also promote healthy vegetative growth.
Soil Amendments: Adding amendments like bat guano or blood meal can enhance nitrogen levels, supporting vigorous leaf and stem growth.
Pre-Flowering Stage (Week 5-6)
Nutrient Needs
As the plant transitions from vegetative growth to flowering, nutrient requirements shift. Introducing bloom nutrients, such as phosphorus and potassium, during this pre-flowering stage is critical for setting the foundation for bud development.
Macronutrients: Decrease nitrogen, increase phosphorus and potassium.
Micronutrients: Maintain levels of calcium, magnesium, and iron to support structural development and enzyme functions.
Nutrient Options
Transition Fertilizer: Use a fertilizer with a higher phosphorus and potassium ratio, such as 2-4-4 or 1-3-2. Products like Advanced Nutrients Iguana Juice Bloom can be effective.
Organic Options: Bone meal and kelp extract can be excellent organic sources for phosphorus and potassium. Introducing humic and fulvic acids can also enhance nutrient uptake.
Flowering Stage (Week 7-10+)

Nutrient Needs
During flowering, autoflowering cannabis plants focus energy on bud formation. Phosphorus and potassium are crucial for flower development, while excessive nitrogen can hinder bud growth.
Macronutrients: Low nitrogen, high phosphorus, and potassium.
Micronutrients: Essential micronutrients should be continued to support overall plant health and robust flower production.
Nutrient Options
Flowering Fertilizer: Utilize a bloom-specific fertilizer with an N-P-K ratio like 1-3-3 or 0-5-4.
Organic Options: Bone meal, bat guano, and liquid seaweed are excellent for organic blooming nutrients. Introducing molasses during the late flowering stage can provide additional carbohydrates and micronutrients to enhance resin production.
Supplemental Additives: Products like silica can strengthen cell walls, and beneficial microbes can enhance nutrient availability and root health.
Effective nutrient management for autoflowering cannabis plants involves understanding their unique growth cycle and providing the right nutrients at each stage. From minimal nutrient needs during the seedling stage to increased demands during vegetative growth and flowering, adjusting nutrient intake is key to achieving healthy plants and bountiful harvests.
Caveats and Signs to Watch For
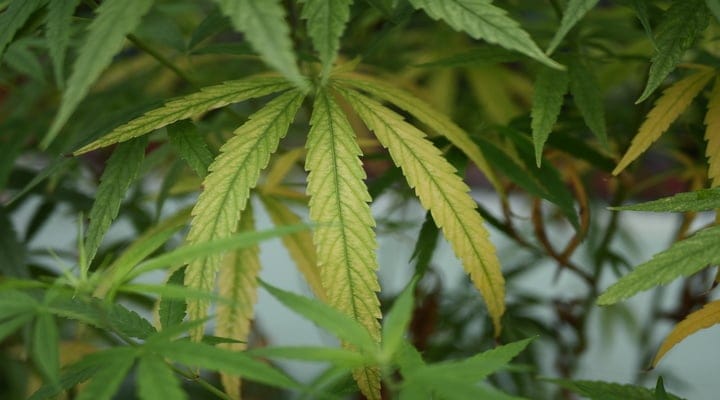

Nutrient Burn: Symptoms include yellowing or browning leaf tips and edges. This is often a sign of over-fertilization. Flush the soil with plain water to mitigate this issue.
Nutrient Deficiency: Symptoms include:
Nitrogen Deficiency: Yellowing of older leaves starting at the bottom.
Phosphorus Deficiency: Dark green or purple leaves, stunted growth.
Potassium Deficiency: Yellowing at the leaf edges, brown spots.
Magnesium Deficiency: Yellowing between leaf veins.
pH Levels: Ensure the pH of your water and nutrient solution is between 6.0-6.5 to facilitate optimal nutrient uptake. Regularly check and adjust the pH as needed.
Environmental Factors: Temperature, humidity, and light intensity also affect nutrient needs. Maintain optimal conditions (temperature: 70-85°F, humidity: 40-60% during vegetative stage, 40-50% during flowering) to support plant health.
Conclusion
Autoflowering cannabis plants have different nutrient requirements than photoperiod plants. While the necessary nutrients are the same, autflower nutrient quanities differ due to the size of the lant and shorter lifecycle. By adhering to these guidelines and paying close attention to the plant's signals, growers can ensure their autoflowering cannabis plants thrive and produce high-quality yields. Happy growing!


